Identifying microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in colorectal cancer by a combination of expression profile and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 22703586
- PMCID: PMC3418553
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-68
Identifying microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in colorectal cancer by a combination of expression profile and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in carcinogenesis and tumor progression by regulating post-transcriptional gene expression. However, the miRNA-mRNA regulatory network is far from being fully understood. The objective of this study is to identify the colorectal cancer (CRC) specific miRNAs and their target mRNAs using a multi-step approach.
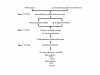
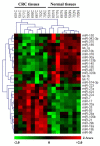
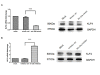
Results: A multi-step approach combining microarray miRNA and mRNA expression profile and bioinformatics analysis was adopted to identify the CRC specific miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. First, 32 differentially expressed miRNAs and 2916 mRNAs from CRC samples and their corresponding normal epithelial tissues were identified by miRNA and mRNA microarray, respectively. Secondly, 22 dysregulated miRNAs and their 58 target mRNAs (72 miRNA-mRNA pairs) were identified by a combination of Pearson's correlation analysis and prediction by databases TargetScan and miRanda. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that these miRNA-mRNAs pairs were involved in Wnt signaling pathway. Additionally, 6 up-regulated miRNAs (mir-21, mir-223, mir-224, mir-29a, mir-29b, and mir-27a) and 4 down-regulated predicted target mRNAs (SFRP1, SFRP2, RNF138, and KLF4) were selected to validate the expression level and their anti-correlationship in an extended cohort of CRC patients by qRT-PCR. Except for mir-27a, the differential expression and their anti-correlationship were proven. Finally, a transfection assay was performed to validate a regulatory relationship between mir-29a and KLF4 at both RNA and protein levels.
Conclusions: Seventy-two miRNA-mRNA pairs combined by 22 dysregulated miRNAs and their 58 target mRNAs identified by the multi-step approach appear to be involved in CRC tumorigenesis. The results in our study were worthwhile to further investigation via a functional study to fully understand the underlying regulatory mechanisms of miRNA in CRC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic analysis reveals an exosomal miRNA-mRNA network in colorectal cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Feb 27;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00905-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33639954 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of a long non-coding RNA LIFR-AS1/miR-29a/TNFAIP3 axis in colorectal cancer resistance to pohotodynamic therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Sep;1864(9 Pt B):2871-2880. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.05.020. Epub 2018 May 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29807108
-
Identifying the key genes and microRNAs in colorectal cancer liver metastasis by bioinformatics analysis and in vitro experiments.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jan;41(1):279-291. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6840. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30542696 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Clusters with Down-Regulated Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer and Their Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 29;21(13):4633. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134633. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32610706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis of miRNA-mRNA expression in the brain during high temperature-induced masculinization of female Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Genomics. 2024 May;116(3):110856. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110856. Epub 2024 May 10. Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38734154 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-224 is associated with colorectal cancer progression and response to 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy by KRAS-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Br J Cancer. 2015 Apr 28;112(9):1480-90. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.125. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25919696 Free PMC article.
-
Rheb-mTOR activation rescues Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and memory function by restoring miR-146 activity in glial cells.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Apr 24;24:868-887. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.04.008. eCollection 2021 Jun 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34094708 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering MicroRNA-Regulatory Modules in Multi-Dimensional Cancer Genomic Data: A Survey of Computational Methods.Cancer Inform. 2016 Oct 3;15(Suppl 2):25-42. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S39369. eCollection 2016. Cancer Inform. 2016. PMID: 27721651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).Leuk Res. 2013 Nov;37(11):1420-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Leuk Res. 2013. PMID: 24054860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational analysis reveals microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Dec;36(6):834-838. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1671-y. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27924512
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

