Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to a novel Trp101Stop myelin protein zero mutation associated with debilitating neuropathic pain
- PMID: 22704856
- PMCID: PMC3399778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.05.015
Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to a novel Trp101Stop myelin protein zero mutation associated with debilitating neuropathic pain
Abstract
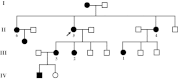
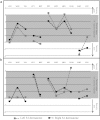
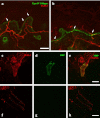
We report an English kindred affected across 4 generations with a hereditary neuropathy associated with debilitating neuropathic pain as the main clinical feature. The principal finding on clinical examination was sensory loss, and there was variable motor dysfunction. Electrophysiological studies revealed mild features of demyelination with median conduction velocity in the intermediate range. There was an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance, and genetic testing revealed a novel heterozygous Trp101X mutation in exon 3 coding for a portion of the extracellular domain of myelin protein zero. This is predicted to lead to premature termination of translation. Myelin protein zero is a key structural component of compact myelin, and over 100 mutations in this protein have been reported, which can give rise to neuropathies with either axonal, demyelinating, or intermediate features encompassing a wide range of severity. Chronic pain is an increasingly recognised sequela of certain hereditary neuropathies and may be musculoskeletal or neuropathic in origin. In this kindred, the neuropathy was relatively mild in severity, however, neuropathic pain was an important and disabling outcome.
Copyright © 2012 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Atanasoski S., Scherer S.S., Nave K.A., Suter U. Proliferation of Schwann cells and regulation of cyclin D1 expression in an animal model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. J Neurosci Res. 2002;67:443–449. - PubMed
-
- Burns T.M., Phillips L.H., 2nd, Dimberg E.L., Vaught B.K., Klein C.J. Novel myelin protein zero mutation (Arg36Trp) in a patient with acute onset painful neuropathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2006;16:308–310. - PubMed
-
- Carter G.T., Jensen M.P., Galer B.S., Kraft G.H., Crabtree L.D., Beardsley R.M., Abresch R.T., Bird T.D. Neuropathic pain in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79:1560–1564. - PubMed
-
- Dawkins J.L., Hulme D.J., Brahmbhatt S.B., Auer-Grumbach M., Nicholson G.A. Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Nat Genet. 2001;27:309–312. - PubMed
-
- Dubner R., Sumino R., Wood W.I. A peripheral “cold” fiber population responsive to innocuous and noxious thermal stimuli applied to monkey’s face. J Neurophysiol. 1975;38:1373–1389. - PubMed

