Recent progress in structure-based anti-influenza drug design
- PMID: 22704956
- PMCID: PMC3459301
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.06.002
Recent progress in structure-based anti-influenza drug design
Abstract
Seasonal and pandemic influenza have caused high morbidity and mortality worldwide. Recent emergence of influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 strains has heightened concern, especially as a result of their drug resistance. The life cycle of influenza viruses has been well studied and nearly all the viral proteins are becoming potential therapeutic targets. In this review, we present an overview of recent progress in structure-based anti-influenza drug design, paying close attention to the increasing role of computation and strategies for overcoming drug resistance.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
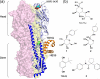
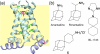




References
-
- World Health Organization Website http://www.who.int/
-
- Cox NJ, Subbarao K. Global epidemiology of influenza: past and present. Annu. Rev. Med. 2000;51:407–421. - PubMed
-
- Gubareva LV, et al. Selection of influenza virus mutants in experimentally infected volunteers treated with oseltamivir. J. Infect. Dis. 2001;183:523–531. - PubMed
-
- Gubareva L, et al. Update: drug susceptibility of swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) viruses, April 2009. Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2009;58:433–435. - PubMed
-
- Palese P, Young JF. Variation of influenza A, B, and C viruses. Science. 1982;215:1468–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

