Delayed fusion and altered gene expression contribute to semicircular canal defects in Chd7 deficient mice
- PMID: 22705977
- PMCID: PMC3477510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.06.002
Delayed fusion and altered gene expression contribute to semicircular canal defects in Chd7 deficient mice
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Delayed fusion and altered gene expression contribute to semicircular canal defects in Chd7 deficient mice" [Mech. Dev. 129 (9-12) (2012) 308-23 (PMID 22705977)].Cells Dev. 2022 Jun;170:203779. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2022.203779. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Cells Dev. 2022. PMID: 35453010 No abstract available.
Abstract
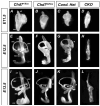
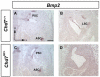
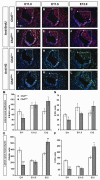
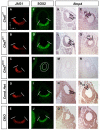
Proper morphogenesis of inner ear semicircular canals requires precise regulation of cellular proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and fusion of epithelial plates. Epigenetic regulation of these processes is not well understood, but is likely to involve chromatin remodeling enzymes. CHD7 is a chromodomain-containing, ATP dependent helicase protein that is highly expressed in the developing ear and is required for semicircular canal development in both humans and mice. Here we report that mice with heterozygous loss of Chd7 function exhibit delayed semicircular canal genesis, delayed Netrin1 expression and disrupted expression of genes that are critical for semicircular canal formation (Bmp2, Bmp4, Msx1 and Fgf10). Complete loss of Chd7 results in aplasia of the semicircular canals and sensory vestibular organs, with reduced or absent expression of Otx1, Hmx3, Jagged1, Lmo4, Msx1 and Sox2. Our results suggest that Chd7 may have critical selector gene functions during inner ear morphogenesis. Detailed analysis of the epigenetic modifications underlying these gene expression changes should provide insights into semicircular canal development and help in the design of therapies for individuals with inner ear malformations.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Defects in vestibular sensory epithelia and innervation in mice with loss of Chd7 function: implications for human CHARGE syndrome.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Oct 10;504(5):519-32. doi: 10.1002/cne.21460. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17701983
-
Netrin 1 is required for semicircular canal formation in the mouse inner ear.Development. 2000 Jan;127(1):13-22. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.1.13. Development. 2000. PMID: 10654596
-
Distinct functions for netrin 1 in chicken and murine semicircular canal morphogenesis.Development. 2017 Sep 15;144(18):3349-3360. doi: 10.1242/dev.144519. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Development. 2017. PMID: 28851705 Free PMC article.
-
CHD7 and SOX2 act in a common gene regulatory network during mammalian semicircular canal and cochlear development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2311720121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2311720121. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38408234 Free PMC article.
-
Inner ear manifestations in CHARGE: Abnormalities, treatments, animal models, and progress toward treatments in auditory and vestibular structures.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017 Dec;175(4):439-449. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31587. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 29082607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CHD7 interacts with BMP R-SMADs to epigenetically regulate cardiogenesis in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Apr 15;23(8):2145-56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt610. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24293546 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Causes of Inner Ear Anomalies: a Review from the Turkish Study Group for Inner Ear Anomalies.Balkan Med J. 2019 Jul 11;36(4):206-211. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2019.2019.4.66. Epub 2019 May 27. Balkan Med J. 2019. PMID: 31131597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary analysis of genes associated with the sense of balance in semi-aquatic mammals.BMC Ecol Evol. 2025 Jan 10;25(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12862-024-02345-9. BMC Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 39794719 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed analysis of chick optic fissure closure reveals Netrin-1 as an essential mediator of epithelial fusion.Elife. 2019 Jun 4;8:e43877. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43877. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31162046 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into inner ear-specific gene regulation: Epigenetics and non-coding RNAs in inner ear development and regeneration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 May;65:69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27836639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acampora D, Mazan S, Avantaggiato V, Barone P, Tuorto F, Lallemand Y, Brulet P, Simeone A. Epilepsy and brain abnormalities in mice lacking the Otx1 gene. Nature Genetics. 1996;14:218–22. - PubMed
-
- Adams ME, Hurd EA, Beyer LA, Swiderski DL, Raphael Y, Martin DM. Defects in vestibular sensory epithelia and innervation in mice with loss of Chd7 function: implications for human CHARGE syndrome. J Comp Neurol. 2007;504:519–32. - PubMed
-
- Alsina B, Giraldez F, Pujades C. Patterning and cell fate in ear development. Int J Dev Biol. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bok J, Chang W, Wu DK. Patterning and morphogenesis of the vertebrate inner ear. Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51:521–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

