Rare TP53 genetic variant associated with glioma risk and outcome
- PMID: 22706378
- PMCID: PMC3576847
- DOI: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-100941
Rare TP53 genetic variant associated with glioma risk and outcome
Abstract
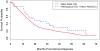
Validation of a recent finding linking a rare variant in TP53 to the risk of glioma, the most common primary brain tumour, is reported here. This study genotyped the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs78378222 in 566 glioma cases and 603 controls. The variant 'C' allele (with an allelic frequency of 1.1% in controls) was associated with a 3.5-fold excess in glioma risk (odds ratio 3.54; p=0.0001). Variant carriers had significantly improved survival (hazard ratio 0.52; p=0.009) when compared to non-carriers. The rs78378222 SNP is the first confirmed rare susceptibility variant in glioma. Results may shed light on the aetiology and progression of these tumours.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bodmer W, Tomlinson I. Rare genetic variants and the risk of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Jun;20(3):262–7. Review. - PubMed
-
- Stacey SN, Sulem P, Jonasdottir A, Masson G, Gudmundsson J, Gudbjartsson DF, Magnusson OT, Gudjonsson SA, Sigurgeirsson B, Thorisdottir K, Ragnarsson R, Benediktsdottir KR, Nexø BA, Tjønneland A, Overvad K, Rudnai P, Gurzau E, Koppova K, Hemminki K, Corredera C, Fuentelsaz V, Grasa P, Navarrete S, Fuertes F, García-Prats MD, Sanambrosio E, Panadero A, De Juan A, Garcia A, Rivera F, Planelles D, Soriano V, Requena C, Aben KK, van Rossum MM, Cremers RG, van Oort IM, van Spronsen DJ, Schalken JA, Peters WH, Helfand BT, Donovan JL, Hamdy FC, Badescu D, Codreanu O, Jinga M, Csiki IE, Constantinescu V, Badea P, Mates IN, Dinu DE, Constantin A, Mates D, Kristjansdottir S, Agnarsson BA, Jonsson E, Barkardottir RB, Einarsson GV, Sigurdsson F, Moller PH, Stefansson T, Valdimarsson T, Johannsson OT, Sigurdsson H, Jonsson T, Jonasson JG, Tryggvadottir L, Rice T, Hansen HM, Xiao Y, Lachance DH, O Neill BP, Kosel ML, Decker PA, Thorleifsson G, Johannsdottir H, Helgadottir HT, Sigurdsson A, Steinthorsdottir V, Lindblom A, Sandler RS, Keku TO, Banasik K, Jørgensen T, Witte DR, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Jinga V, Neal DE, Catalona WJ, Wrensch M, Wiencke J, Jenkins RB, Nagore E, Vogel U, Kiemeney LA, Kumar R, Mayordomo JI, Olafsson JH, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Rafnar T, Stefansson K Swedish Low-risk Colorectal Cancer Study Group. A germline variant in the TP53 polyadenylation signal confers cancer susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2011 Sep 25;43(11):1098–103. doi: 10.1038/ng.926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous