Is fixation failure after plate fixation of the symphysis pubis clinically important?
- PMID: 22707071
- PMCID: PMC3392398
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-012-2427-z
Is fixation failure after plate fixation of the symphysis pubis clinically important?
Abstract
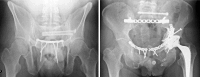
Background: Plate fixation is a recognized treatment for pelvic ring injuries involving disruption of the pubic symphysis. Although fixation failure is well known, it is unclear whether early or late fixation failure is clinically important.
Questions/purposes: We therefore determined (1) the incidence and mode of failure of anterior plate fixation for traumatic pubic symphysis disruption; (2) whether failure of fixation was associated with the types of pelvic ring injury or pelvic fixation used; (3) the complications, including the requirement for reoperation or hardware removal; and (4) whether radiographic followup of greater than 1 year alters subsequent management.
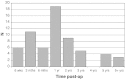
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 148 of 178 (83%) patients with traumatic symphysis pubis diastasis treated by plate fixation between 1994 and 2008. Routine radiographic review, pelvic fracture classification, method of fixation, incidence of fixation failure, timing and mode of failure, and the complications were recorded after a minimum followup of 12 months (mean, 45 months; range, 1-14 years).
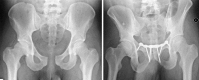
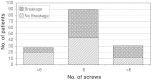
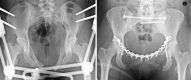
Results: Hardware breakage occurred in 63 patients (43%), of which 61 were asymptomatic. Breakage was not related to type of plate, fracture classification, or posterior pelvic fixation. Five patients (3%) required revision surgery for failure of fixation or symptomatic instability of the symphysis pubis, and seven patients (5%) had removal of hardware for other reasons, including late deep infection in three (2%). Routine radiographic screening as part of annual followup after 1 year did not alter management.
Conclusions: Our observations suggest the high rate of late fixation failure after plate fixation of the symphysis pubis is not clinically important.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiographic changes of implant failure after plating for pubic symphysis diastasis: an underappreciated reality?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012 Aug;470(8):2148-53. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2340-5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012. PMID: 22552765 Free PMC article.
-
Variables associated with loss of reduction after plate fixation of pubic symphysis injuries.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 Mar 17;35(1):120. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04240-5. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40097727
-
Comparative study between anterior symphyseal platting and percutaneous symphyseal screws for treatment of traumatic symphyseal diastasis.Int Orthop. 2025 Mar;49(3):755-765. doi: 10.1007/s00264-025-06446-y. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Int Orthop. 2025. PMID: 39954052 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in treatment of pubic symphysis diastasis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;28(2):250-4. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24796204 Review. Chinese.
-
Traumatic Diastasis of the Pubic Symphysis-A Review of Fixation Method Outcomes.Surg Technol Int. 2016 Oct 26;29:265-269. Surg Technol Int. 2016. PMID: 27466875 Review.
Cited by
-
Fixation failure in patients with traumatic diastasis of pubic symphysis: impact of loss of reduction on early functional outcomes.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Nov 6;16(1):661. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02802-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34742331 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Biomechanical Characteristics and Pelvic Ring Stability Using Different Fixation Methods to Treat Pubic Symphysis Diastasis: A Finite Element Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Dec;94(49):e2207. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002207. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26656353 Free PMC article.
-
Transobturator-cable-fixation in pelvic ring injuries with symphyseal disruption - a last resort?Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Oct;50(5):2559-2567. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02578-9. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 39112763 Free PMC article.
-
The role of anterior supra-acetabular external fixator as definitive treatment for anterior ring fixation in unstable pelvic fractures.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022 Oct;48(5):3737-3746. doi: 10.1007/s00068-021-01711-2. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022. PMID: 34097076
-
Do we need another screw? Sacroiliac screw fixation in open-book pelvic ring injuries (APC type II).EFORT Open Rev. 2024 Aug 1;9(8):827-836. doi: 10.1530/EOR-23-0173. EFORT Open Rev. 2024. PMID: 39087500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassam D, Cephas GA, Ferguson KA, Beard LN, Young JS. A protocol for the initial management of unstable pelvic fractures. Am Surg. 1998;64:862–867. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

