Hypermethylation-mediated silencing of p14(ARF) in fibroblasts from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22707614
- PMCID: PMC6189747
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00332.2011
Hypermethylation-mediated silencing of p14(ARF) in fibroblasts from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
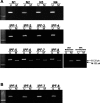
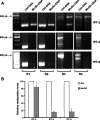
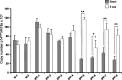
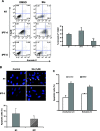
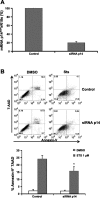
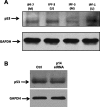
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating lung disease of unknown etiology. A conspicuous feature is the formation and persistence of fibroblastic/myofibroblastic foci throughout the lung parenchyma. Mechanisms remain unknown, but data indicate that fibroblasts acquire an antiapoptotic phenotype. We hypothesized that transcriptional silencing of proapoptotic genes may be implicated, and accordingly we evaluated the epigenetic regulation of p14(ARF). The expression of p14(ARF) was analyzed by RT-PCR in IPF (n = 8) and normal derived fibroblasts (n = 4) before and after treatment with 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-aza) and trichostatin A (TSA). p14(ARF) gene promoter methylation was determined by methylation-specific PCR (MS-PCR) and by DNA digestion with endonuclease McrBc, which cleaves 50% of methylated CpG. Apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin-V and nuclear staining. p14(ARF) expression was significantly decreased in four of the eight IPF fibroblasts lines, which was restored after 5-aza treatment. No changes were found with TSA. MS-PCR of bisulfite-treated genomic DNA showed a correlation between the reduced expression of p14(ARF) and the presence of hypermethylated promoter. No amplification was observed in the DNA treated with the McrBc enzyme, corroborating promoter hypermethylation. p14(ARF)-hypermethylated IPF fibroblasts were significantly more resistant to staurosporine-and S-nitrosoglutathione-induced apoptosis compared with normal and nonmethylated IPF fibroblasts (P < 0.01) and showed reduced levels of p53. Resistance to apoptosis was provoked in fibroblasts when p14(ARF) expression was inhibited by siRNA (P < 0.05). These findings demonstrate that many IPF fibroblasts have reduced expression of the proapoptotic p14(ARF) attributable to promoter hypermethylation and indicate that epigenetic mechanisms may underlie their resistance to apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the p14ARF promoter by DNA methylation.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jan 1;7(1):112-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.1.5137. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18196972
-
Biological significance of promoter hypermethylation of p14/ARF gene: relationships to p53 mutational status in Tunisian population with colorectal carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2014 Feb;35(2):1439-49. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1198-9. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24065196 Free PMC article.
-
Wip1 over-expression correlated with TP53/p14(ARF) pathway disruption in human astrocytomas.J Surg Oncol. 2011 Nov 1;104(6):679-84. doi: 10.1002/jso.22004. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21695702
-
Epigenetics in lung fibrosis: from pathobiology to treatment perspective.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015 Sep;21(5):454-62. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000191. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015. PMID: 26176965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Epigenomics. 2012 Apr;4(2):195-203. doi: 10.2217/epi.12.10. Epigenomics. 2012. PMID: 22449190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics and the overhealing wound: the role of DNA methylation in fibrosis.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015 Oct 1;8:18. doi: 10.1186/s13069-015-0035-8. eCollection 2015. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2015. PMID: 26435749 Free PMC article.
-
Deficient repair response of IPF fibroblasts in a co-culture model of epithelial injury and repair.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2014 Apr 29;7:7. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-7-7. eCollection 2014. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2014. PMID: 24834127 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast and myofibroblast activation in normal tissue repair and fibrosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Aug;25(8):617-638. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00716-0. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38589640 Review.
-
Transcriptomic and Epigenetic Profiling of Fibroblasts in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Jan;66(1):53-63. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0437OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34370624 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a Unified Approach in Autoimmune Fibrotic Signalling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 21;24(10):9060. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109060. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badal V , Menendez S , Coomber D , Lane DP. Regulation of the p14ARF promoter by DNA methylation. Cell Cycle : 112–119, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Charles Sherr J. The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res : 3689–3695, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Esteller M , Tortola S , Toyota M , Capella G , Peinado MA , Baylin SB , Herman JG. Hypermethylation-associated inactivation of p14ARF is independent of p16INK4a methylation and p53 mutational status. Cancer Res : 129–133, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Eymin B , Karayan L , Séité P , Brambilla C , Brambilla E , Larsen CJ , Gazzéri S. Human ARF binds E2F1 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Oncogene : 1033–1041, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

