Disseminated cutaneous histoplasmosis in an immunocompetent adult
- PMID: 22707773
- PMCID: PMC3371525
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.96194
Disseminated cutaneous histoplasmosis in an immunocompetent adult
Abstract
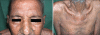
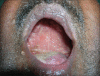
Histoplasmosis, a systemic mycosis caused by the dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum var capsulatum and Histoplasma capsulatum var duboisii is endemic to many parts of the world. The clinical manifestations range from acute or chronic pulmonary infection to a progressive disseminated disease. After initial exposure to the fungus, the infection is self-limited and restricted to the lungs in 99% of healthy individuals. The remaining 1%, however, progress to either disseminated or chronic disease involving the lungs, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow or rarely, the skin and mucous membranes. Mucocutaneous histoplasmosis is frequently reported in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), but it is rare in immunocompetent hosts. A 60-year-old male presented with asymptomatic swelling of the hard palate and crusted papules and nodules over the extremities, face and trunk. Clinically, the diagnoses of cutaneous cryptococcosis versus histoplasmosis was considered in this patient. A chest X-ray revealed hilar lymphadenopathy. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was nonreactive. Skin biopsy revealed multiple tiny intracellular round yeast forms with a halo in the mid-dermis. Culture of the skin biopsy in Sabouraud's dextrose agar showed colonies of Histoplasma capsulatum. Despite an investigation including no evidence of underlying immunosuppression was found, he was started on IV amphotericin-B (0.5 mg/kg/day). However, the patient succumbed to his disease 2 days after presentation. We report a rare case of disseminated cutaneous histoplasmosis in an immunocompetent individual.
Keywords: Histoplasmosis; histoplasma capsulatum; immunocompetent; mucocutaneous lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Hay RJ, Moore M. Mycology. In: Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, Breathnach SM, editors. Rook/Wilkinson/Ebling Textbook of dermatology. 6th ed. Oxford: Oxford Blackwell Science; 1998. pp. 1363–6.
-
- Sanyal M, Thammaya Skin sensitivity to histoplasmin in Calcutta and its neighborhood. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1980;46:94–8. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee AM, Khan KP, Sanyal M, Basu N. Histoplasmosis in India with report of two cases. J Ind Med Assoc. 1971;56:121–5. - PubMed
-
- Gugnani HC. Histoplasmosis in Africa Indian. J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2000;42:271–7. - PubMed
-
- Saoji AM, Grover S, Mene AR, Patoria NK, Sharma KD. Histoplasmosis. J Indian Med Assoc. 1976;66:37–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
