Cholinergic modulation of cognitive processing: insights drawn from computational models
- PMID: 22707936
- PMCID: PMC3374475
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00024
Cholinergic modulation of cognitive processing: insights drawn from computational models
Abstract
Acetylcholine plays an important role in cognitive function, as shown by pharmacological manipulations that impact working memory, attention, episodic memory, and spatial memory function. Acetylcholine also shows striking modulatory influences on the cellular physiology of hippocampal and cortical neurons. Modeling of neural circuits provides a framework for understanding how the cognitive functions may arise from the influence of acetylcholine on neural and network dynamics. We review the influences of cholinergic manipulations on behavioral performance in working memory, attention, episodic memory, and spatial memory tasks, the physiological effects of acetylcholine on neural and circuit dynamics, and the computational models that provide insight into the functional relationships between the physiology and behavior. Specifically, we discuss the important role of acetylcholine in governing mechanisms of active maintenance in working memory tasks and in regulating network dynamics important for effective processing of stimuli in attention and episodic memory tasks. We also propose that theta rhythm plays a crucial role as an intermediary between the physiological influences of acetylcholine and behavior in episodic and spatial memory tasks. We conclude with a synthesis of the existing modeling work and highlight future directions that are likely to be rewarding given the existing state of the literature for both empiricists and modelers.
Keywords: acetylcholine; attention; computational model; entorhinal cortex; memory; oscillatory interference; spatial navigation; theta.
Figures

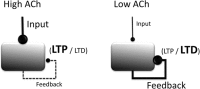
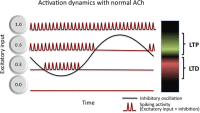

References
-
- Alkondon M., Pereira E. F., Barbosa C. T., Albuquerque E. X. (1997). Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation modulates gamma-aminobutyric acid release from CA1 neurons of rat hippocampal slices. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 1396–1411 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

