Controlling Parasympathetic Regulation of Heart Rate: A Gatekeeper Role for RGS Proteins in the Sinoatrial Node
- PMID: 22707940
- PMCID: PMC3374348
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00204
Controlling Parasympathetic Regulation of Heart Rate: A Gatekeeper Role for RGS Proteins in the Sinoatrial Node
Abstract
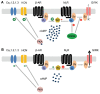
Neurotransmitters released from sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve terminals in the sinoatrial node (SAN) exert their effects via G-protein-coupled receptors. Integration of these different G-protein signals within pacemaker cells of the SAN is critical for proper regulation of heart rate and function. For example, excessive parasympathetic signaling can be associated with sinus node dysfunction (SND) and supraventricular arrhythmias. Our previous work has shown that one member of the regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) protein family, RGS4, is highly and selectively expressed in pacemaker cells of the SAN. Consistent with its role as an inhibitor of parasympathetic signaling, RGS4-knockout mice have reduced basal heart rates and enhanced negative chronotropic responses to parasympathetic agonists. Moreover, RGS4 appears to be an important part of SA nodal myocyte signaling pathways that mediate G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channel (GIRK) channel activation/deactivation and desensitization. Since RGS4 acts immediately downstream of M2 muscarinic receptors, it is tempting to speculate that RGS4 functions as a master regulator of parasympathetic signaling upstream of GIRKs, HCNs, and L-type Ca(2+) channels in the SAN. Thus, loss of RGS4 function may lead to increased susceptibility to conditions associated with increased parasympathetic signaling, including bradyarrhythmia, SND, and atrial fibrillation.
Keywords: GIRK channels; RGS protein; bradyarrhythmia; parasympathetic signaling; sinoatrial node.
Figures
References
-
- Aistrup G. L., Cokic I., Ng J., Gordon D., Koduri H., Browne S., Arapi D., Segon Y., Goldstein J., Angulo A., Wasserstrom J. A., Goldberger J. J., Kadish A. H., Arora R. (2011). Targeted nonviral gene-based inhibition of Galpha(i/o)-mediated vagal signaling in the posterior left atrium decreases vagal-induced atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 8, 1722–1729 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.06.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aistrup G. L., Villuendas R., Ng J., Gilchrist A., Lynch T. W., Gordon D., Cokic I., Mottl S., Zhou R., Dean D. A., Wasserstrom J. A., Goldberger J. J., Kadish A. H., Arora R. (2009). Targeted G-protein inhibition as a novel approach to decrease vagal atrial fibrillation by selective parasympathetic attenuation. Cardiovasc. Res. 83, 481–492 10.1093/cvr/cvp148 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benditt D. G., Sakaguchi S., Goldstein M. A., Lurie K. G., Gornick C. C., Adler S. W. (1995). “Sinus node dysfunction: pathophysiology, clinical features, evaluation, and treatment,” in Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 2nd Edn, eds Zipes D. P., Jalife J. (Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Company; ), 1215–1247
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

