'Ribozoomin'--translation initiation from the perspective of the ribosome-bound eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs)
- PMID: 22708493
- PMCID: PMC3434475
- DOI: 10.2174/138920312801619385
'Ribozoomin'--translation initiation from the perspective of the ribosome-bound eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs)
Abstract
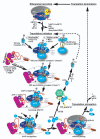
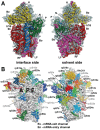
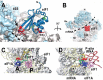
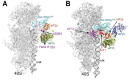
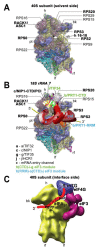
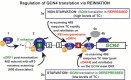
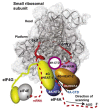
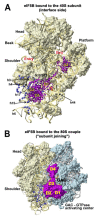
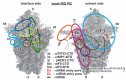
Protein synthesis is a fundamental biological mechanism bringing the DNA-encoded genetic information into life by its translation into molecular effectors - proteins. The initiation phase of translation is one of the key points of gene regulation in eukaryotes, playing a role in processes from neuronal function to development. Indeed, the importance of the study of protein synthesis is increasing with the growing list of genetic diseases caused by mutations that affect mRNA translation. To grasp how this regulation is achieved or altered in the latter case, we must first understand the molecular details of all underlying processes of the translational cycle with the main focus put on its initiation. In this review I discuss recent advances in our comprehension of the molecular basis of particular initiation reactions set into the context of how and where individual eIFs bind to the small ribosomal subunit in the pre-initiation complex. I also summarize our current knowledge on how eukaryotic initiation factor eIF3 controls gene expression in the gene-specific manner via reinitiation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
