Lung ultrasound in the management of acute decompensated heart failure
- PMID: 22708913
- PMCID: PMC3406272
- DOI: 10.2174/157340312801784907
Lung ultrasound in the management of acute decompensated heart failure
Abstract
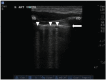
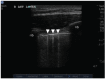
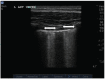
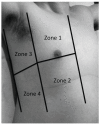
Once thought impracticable, lung ultrasound is now used in patients with a variety of pulmonary processes. This review seeks to describe the utility of lung ultrasound in the management of patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). A literature search was carried out on PubMed/Medline using search terms related to the topic. Over three thousand results were narrowed down via title and/or abstract review. Related articles were downloaded for full review. Case reports, letters, reviews and editorials were excluded. Lung ultrasonographic multiple B-lines are a good indicator of alveolar interstitial syndrome but are not specific for ADHF. The absence of multiple B-lines can be used to rule out ADHF as a causative etiology. In clinical scenarios where the assessment of acute dyspnea boils down to single or dichotomous pathologies, lung ultrasound can help rule in ADHF. For patients being treated for ADHF, lung ultrasound can also be used to monitor response to therapy. Lung ultrasound is an important adjunct in the management of patients with acute dyspnea or ADHF.
Figures






References
-
- Lichtenstein D, Mézière G, Biderman P, Gepner A, Barré O. The comet-tail artifact. An ultrasound sign of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Nov;156(5):1640–6. - PubMed
-
- Wilkerson RG, Stone MB. Sensitivity of bedside ultrasound and supine anteroposterior chest radiographs for the identification of pneumothorax after blunt trauma. Acad Emerg Med. 2010 Jan;17(1):11–7. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein DA, Menu Y. A bedside ultrasound sign ruling out pneumothorax in the critically ill. Lung sliding. Chest. 1995;108:1345–8. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein D, Mezière G, Biderman P, Gepner A. The comet-tail artifact: An ultrasound sign ruling out pneumothorax. Intensive Care Med. 1999 Apr;25(4):383–8. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein D, Mezière G, Biderman P, Gepner A. The" lung point": An ultrasound sign specific to pneumothorax. Intensive Care Medicine. 2000;26(10):1434–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

