Long-term survival and predictors for mortality among dialysis patients in an endemic area for chronic liver disease: a national cohort study in Taiwan
- PMID: 22709415
- PMCID: PMC3422197
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-43
Long-term survival and predictors for mortality among dialysis patients in an endemic area for chronic liver disease: a national cohort study in Taiwan
Abstract
Background: Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are at a higher risk for chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis (LC) and mortality than the general population. Optimal modalities of renal replacement therapy for ESRD patients with concomitant end-stage liver disease remain controversial. We investigated the long-term outcome for chronic liver disease among dialysis patients in an endemic area.
Methods: Using Taiwan's National Health Insurance claim data (NHRI-NHIRD-99182), We performed a longitudinal cohort study to investigate the impact of comorbidities on mortality in dialysis patients. We followed up 11293 incident hemodialysis (HD) and 761 peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients from the start of dialysis until the date of death or the end of database period (December 31, 2008). A Cox proportional hazards model was used to identify the risk factors for all-cause mortality.
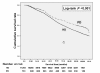
Results: Patients receiving PD tended to be younger and less likely to have comorbidities than those receiving HD. At the beginning of dialysis, a high prevalence rate (6.16 %) of LC was found. Other than well-known risk factors, LC (hazard ratio [HR] 1.473, 95 % CI: 1.329-1.634) and dementia (HR 1.376, 95 % CI: 1.083-1.750) were also independent predictors of mortality. Hypertension and mortality were inversely associated. Dialysis modality and three individual comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, chronic lung disease, and dementia) interacted significantly on mortality risk.
Conclusions: LC is an important predictor of mortality; however, the effect on mortality was not different between HD and PD patients.
Figures
References
-
- United States Renal Data System. Excerpts from the USRDS 2009 annual data report: atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. , ; 2011. http://www.usrds.org (accessed August 25, 2011)
-
- Termorshuizen F, Korevaar JC, Dekker FW, Van Manen JG, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT. NECOSAD Study Group. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: comparison of adjusted mortality rates according to the duration of dialysis: analysis of The Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis 2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2851–2860. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000091585.45723.9E. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical