The male germ cell gene regulator CTCFL is functionally different from CTCF and binds CTCF-like consensus sites in a nucleosome composition-dependent manner
- PMID: 22709888
- PMCID: PMC3418201
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-8
The male germ cell gene regulator CTCFL is functionally different from CTCF and binds CTCF-like consensus sites in a nucleosome composition-dependent manner
Abstract
Background: CTCF is a highly conserved and essential zinc finger protein expressed in virtually all cell types. In conjunction with cohesin, it organizes chromatin into loops, thereby regulating gene expression and epigenetic events. The function of CTCFL or BORIS, the testis-specific paralog of CTCF, is less clear.
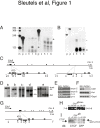
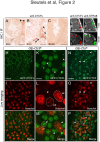
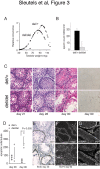
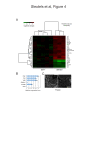
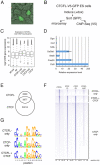
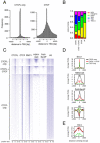
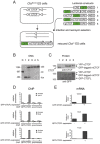
Results: Using immunohistochemistry on testis sections and fluorescence-based microscopy on intact live seminiferous tubules, we show that CTCFL is only transiently present during spermatogenesis, prior to the onset of meiosis, when the protein co-localizes in nuclei with ubiquitously expressed CTCF. CTCFL distribution overlaps completely with that of Stra8, a retinoic acid-inducible protein essential for the propagation of meiosis. We find that absence of CTCFL in mice causes sub-fertility because of a partially penetrant testicular atrophy. CTCFL deficiency affects the expression of a number of testis-specific genes, including Gal3st1 and Prss50. Combined, these data indicate that CTCFL has a unique role in spermatogenesis. Genome-wide RNA expression studies in ES cells expressing a V5- and GFP-tagged form of CTCFL show that genes that are downregulated in CTCFL-deficient testis are upregulated in ES cells. These data indicate that CTCFL is a male germ cell gene regulator. Furthermore, genome-wide DNA-binding analysis shows that CTCFL binds a consensus sequence that is very similar to that of CTCF. However, only ~3,700 out of the ~5,700 CTCFL- and ~31,000 CTCF-binding sites overlap. CTCFL binds promoters with loosely assembled nucleosomes, whereas CTCF favors consensus sites surrounded by phased nucleosomes. Finally, an ES cell-based rescue assay shows that CTCFL is functionally different from CTCF.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that nucleosome composition specifies the genome-wide binding of CTCFL and CTCF. We propose that the transient expression of CTCFL in spermatogonia and preleptotene spermatocytes serves to occupy a subset of promoters and maintain the expression of male germ cell genes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of CTCF and CTCFL in genome regulation through chromatin architecture during the spermatogenesis and carcinogenesis.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 15;12:e18240. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18240. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39430552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the relative and combined contribution of CTCF and CTCFL to genomic regulation.Genome Biol. 2020 May 11;21(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02024-0. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32393311 Free PMC article.
-
BORIS/CTCFL epigenetically reprograms clustered CTCF binding sites into alternative transcriptional start sites.Genome Biol. 2024 Jan 31;25(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03175-0. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38297316 Free PMC article.
-
The Diverging Routes of BORIS and CTCF: An Interactomic and Phylogenomic Analysis.Life (Basel). 2018 Jan 30;8(1):4. doi: 10.3390/life8010004. Life (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29385718 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF and CTCFL in cancer.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Apr;61:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.02.021. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32334335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of CTCF and CTCFL in genome regulation through chromatin architecture during the spermatogenesis and carcinogenesis.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 15;12:e18240. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18240. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39430552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypomethylation of the CTCFL/BORIS promoter and aberrant expression during endometrial cancer progression suggests a role as an Epi-driver gene.Oncotarget. 2014 Feb 28;5(4):1052-61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1697. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24658009 Free PMC article.
-
Brother of regulator of imprinted sites inhibits cisplatin-induced DNA damage in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):251. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12114. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32994814 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the CTCFL Gene during Mouse Embryogenesis Causes Growth Retardation, Postnatal Lethality, and Dysregulation of the Transforming Growth Factor β Pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;35(19):3436-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00381-15. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26169830 Free PMC article.
-
BORIS/CTCFL promotes a switch from a proliferative towards an invasive phenotype in melanoma cells.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Jan 2;6:1. doi: 10.1038/s41420-019-0235-x. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 32123577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartkuhn M, Renkawitz R. Long range chromatin interactions involved in gene regulation. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2008;1783:2161–2166. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro De Almeida C, Heath H, Krpic S, Dingjan GM, Van Hamburg JP, Bergen I, Van De Nobelen S, Sleutels F, Grosveld F, Galjart N, Hendriks RW. Critical role for the transcription regulator CCCTC-binding factor in the control of Th2 cytokine expression. J Immunol. 2009;182:999–1010. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

