Health-related quality of life in different stages of chronic kidney disease and at initiation of dialysis treatment
- PMID: 22710013
- PMCID: PMC3511211
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-10-71
Health-related quality of life in different stages of chronic kidney disease and at initiation of dialysis treatment
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients in different stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD) up to initiation of dialysis treatment and to explore possible correlating and influencing factors.
Methods: Cross-sectional design with 535 patients in CKD stages 2-5 and 55 controls assessed for HRQoL through SF-36 together with biomarkers.
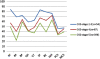
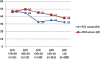
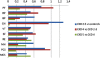
Results: All HRQoL dimensions deteriorated significantly with CKD stages with the lowest scores in CKD 5. The largest differences between the patient groups were seen in 'physical functioning', 'role physical', 'general health' and in physical summary scores (PCS). The smallest disparities were seen in mental health and pain. Patients in CKD stages 2-3 showed significantly decreased HRQoL compared to matched controls, with differences of large magnitude - effect size (ES) ≥ .80 - in 'general health' and PCS. Patients in CDK 4 demonstrated deteriorated scores with a large magnitude in 'physical function', 'general health' and PCS compared to the patients in CKD 2-3. Patients in CKD 5 demonstrated deteriorated scores with a medium sized magnitude (ES 0.5 - 0.79) in 'role emotional' and mental summary scores compared to the patients in CKD 4. Glomerular filtration rate <45 ml/min/1.73 m², age ≥ 61 years, cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥5 mg/L, haemoglobin ≤110 g/L, p-albumin ≤ 35 g/L and overweight were associated with impaired HRQoL. CRP and CVD were the most important predictors of impaired HRQoL, followed by reduced GFR and diabetes.
Conclusions: Having CKD implies impaired HRQoL, also in earlier stages of the disease. At the time for dialysis initiation HRQoL is substantially deteriorated. Co-existing conditions, such as inflammation and cardiovascular disease seem to be powerful predictors of impaired HRQoL in patients with CKD. Within routine renal care, strategies to improve function and well-being considering the management of co-existing conditions like inflammation and CVD need to be developed.
Figures
References
-
- Peterson SJ, Bredow TS. Middle range theories : application to nursing research. 2. Philadelphia, Pa: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009.
-
- NKF. Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. New York: National Kidney Foundation; 2000. [cited 2000]; 2000:[Available from: http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/guidelines_ckd/toc.htm.
-
- ISN, IFKF. World Kidney Day. Brussels: International Society of Nephrology International Federation of Kidney Foundations; 2009. Available from: http://www.worldkidneyday.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

