Neurodevelopmental effects of insulin-like growth factor signaling
- PMID: 22710100
- PMCID: PMC3677055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2012.06.002
Neurodevelopmental effects of insulin-like growth factor signaling
Abstract
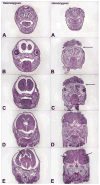
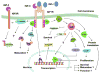
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling greatly impacts the development and growth of the central nervous system (CNS). IGF-I and IGF-II, two ligands of the IGF system, exert a wide variety of actions both during development and in adulthood, promoting the survival and proliferation of neural cells. The IGFs also influence the growth and maturation of neural cells, augmenting dendritic growth and spine formation, axon outgrowth, synaptogenesis, and myelination. Specific IGF actions, however, likely depend on cell type, developmental stage, and local microenvironmental milieu within the brain. Emerging research also indicates that alterations in IGF signaling likely contribute to the pathogenesis of some neurological disorders. This review summarizes experimental studies and shed light on the critical roles of IGF signaling, as well as its mechanisms, during CNS development.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Palmer TD, Alborn AM, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Rosengren LE, Olsson T, Gage FH, Eriksson PS. IGF-I has a direct proliferative effect in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003a;24:23–40. - PubMed
-
- Aberg ND, Blomstrand F, Aberg MA, Bjorklund U, Carlsson B, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Ronnback L, Eriksson PS. Insulin-like growth factor-I increases astrocyte intercellular gap junctional communication and connexin43 expression in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 2003b;74:12–22. - PubMed
-
- Aberg ND, Johansson UE, Aberg MA, Hellstrom NA, Lind J, Bull C, Isgaard J, Anderson MF, Oscarsson J, Eriksson PS. Peripheral infusion of insulin-like growth factor-I increases the number of newborn oligodendrocytes in the cerebral cortex of adult hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 2007;148:3765–3772. - PubMed
-
- Abuzzahab MJ, Schneider A, Goddard A, Grigorescu F, Lautier C, Keller E, Kiess W, Klammt J, Kratzsch J, Osgood D, Pfaffle R, Raile K, Seidel B, Smith RJ, Chernausek SD. IGF-I receptor mutations resulting in intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation. New Engl J Med. 2003;349:2211–2222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

