Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biomarkers in a sandwich immunoassay format using a waveguide-based optical biosensor
- PMID: 22710249
- PMCID: PMC3432392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2012.05.009
Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biomarkers in a sandwich immunoassay format using a waveguide-based optical biosensor
Abstract
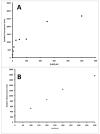
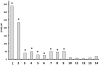
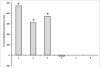
Early diagnosis of active tuberculosis (TB) remains an elusive challenge, especially in individuals with disseminated TB and HIV co-infection. Recent studies have shown a promise for the direct detection of pathogen-specific biomarkers such as lipoarabinomannan (LAM) for the diagnosis of TB in HIV-positive individuals. Currently, traditional immunoassay platforms that suffer from poor sensitivity and high non-specific interactions are used for the detection of such biomarkers. In this manuscript, we demonstrate the development of sandwich immunoassays for the direct detection of three TB-specific biomarkers, namely LAM, early secretory antigenic target 6 (ESAT6) and antigen 85 complex (Ag85), using a waveguide-based optical biosensor platform. Combining detection within the evanescent field of a planar optical waveguide with functional surfaces that reduce non-specific interactions allows for the ultra-sensitive and quantitative detection of biomarkers (an order of magnitude enhanced sensitivity, as compared to plate-based ELISA) in complex patient samples (urine, serum) within a short time. We also demonstrate the detection of LAM in urine from a small sample of subjects being treated for TB using this approach with excellent sensitivity and 100% corroboration with disease status. These results suggest that pathogen-specific biomarkers can be applied for the rapid and effective diagnosis of disease. It is likely that detection of a combination of biomarkers offers greater reliability of diagnosis, rather than detection of any single pathogen biomarker. NCT00341601.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
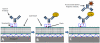
References
-
- Global tuberculosis control: WHO report. 2011.
-
- Dye C, Watt CJ, Bleed DM, Hosseini SM, Raviglione MC. Evolution of tuberculosis control and prospects for reducing tuberculosis incidence, prevalence, and deaths globally. JAMA. 2005;293:2767–2775. - PubMed
-
- Getahun H, Harrington M, O’Brien R, Nunn P. Diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in people with HIV infection or AIDS in resource-constrained settings: informing urgent policy changes. Lancet. 2007;369:2042–2049. - PubMed
-
- Zwerling A, van den Hof S, Scholten J, Cobelens F, Menzies D, Pai M. Interferon-gamma release assays for tuberculosis screening of healthcare workers: a systematic review. Thorax. 2012;67:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Talaat RM, Radwan GS, Mosaad AA, Saleh AS, Bassiouny K. Rapid immunodiagnostic assays for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis infection. Health. 2010;2:171–176.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

