Peptide inhibitors: Four of a kind beats a pair
- PMID: 22710307
- PMCID: PMC3688271
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1000
Peptide inhibitors: Four of a kind beats a pair
Abstract
The proapoptotic cysteine protease caspase-6 participates in the neuropathology of several diseases. Unlike the active dimeric form, the caspase-6 zymogen forms a unique tetramer that can be stabilized by allosteric inhibitors, which prevents caspase-6 activation.
Figures
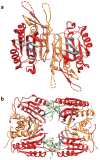
Comment on
-
Allosteric peptides bind a caspase zymogen and mediate caspase tetramerization.Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Jul;8(7):655-60. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.967. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Nat Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22683611
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

