Hepatic stem cells and transforming growth factor β in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 22710573
- PMCID: PMC3745216
- DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.114
Hepatic stem cells and transforming growth factor β in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
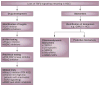
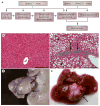
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and lethal cancers worldwide. It arises from modulation of multiple genes by mutations, epigenetic regulation, noncoding RNAs and translational modifications of encoded proteins. Although >40% of HCCs are clonal and thought to arise from cancer stem cells (CSCs), the precise identification and mechanisms of CSC formation remain poorly understood. A functional role of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signalling in liver and intestinal stem cell niches has been demonstrated through mouse genetics. These studies demonstrate that loss of TGF-β signalling yields a phenotype similar to a human CSC disorder, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Insights into this powerful pathway will be vital for developing new therapeutics in cancer. Current clinical approaches are aimed at establishing novel cancer drugs that target activated pathways when the TGF-β tumour suppressor pathway is lost, and TGF-β itself could potentially be targeted in metastases. Studies delineating key functional pathways in HCC and CSC formation could be important in preventing this disease and could lead to simple treatment strategies; for example, use of vitamin D might be effective when the TGF-β pathway is lost or when wnt signalling is activated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ferlay J, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:3030–3044. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S27–S34. - PubMed
-
- Sorrell MF, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development conference statement: management of hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49:S4–S12. - PubMed
-
- Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX. The role of signalling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2010;29:4989–5005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 CA130821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA130821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AA019392/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA042857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA106614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2-AA019392/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

