The liver-specific tumor suppressor STAT5 controls expression of the reactive oxygen species-generating enzyme NOX4 and the proapoptotic proteins PUMA and BIM in mice
- PMID: 22711600
- PMCID: PMC3505809
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25900
The liver-specific tumor suppressor STAT5 controls expression of the reactive oxygen species-generating enzyme NOX4 and the proapoptotic proteins PUMA and BIM in mice
Abstract
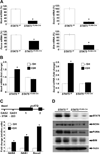
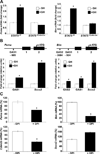
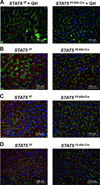
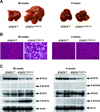
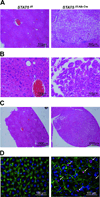
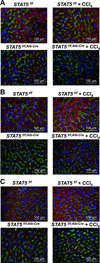
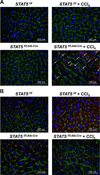
Loss of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) from liver tissue results in steatosis and enhanced cell proliferation. This study demonstrates that liver-specific Stat5-null mice develop severe hepatic steatosis as well as hepatocellular carcinomas at 17 months of age, even in the absence of chemical insults. To understand STAT5's role as a tumor suppressor, we identified and investigated new STAT5 target genes. Expression of Nox4, the gene encoding the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-generating enzyme NOX4, was induced by growth hormone through STAT5. In addition, the genes encoding the proapoptotic proteins PUMA and BIM were induced by growth hormone through STAT5, which bound to GAS motifs in the promoter regions of all three genes. We further show that STAT5-induced activation of Puma and Bim was dependent on NOX4. Treatment of mice with transforming growth factor-β, an inducer of apoptosis, resulted in cleaved caspase-3 in control but not in liver-specific Stat5-null mice. This study demonstrates for the first time that cytokines through STAT5 regulate the expression of the ROS-generating enzyme NOX4 and key proapoptotic proteins.
Conclusion: STAT5 harnesses several distinct signaling pathways in the liver and thereby functions as a tumor suppressor. Besides suppressing the activation of STAT3, STAT5 induces the expression of proapoptotic genes and the production of ROS.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang Q, Wang HY, Liu X, Wasik MA. STAT5A is epigenetically silenced by the tyrosine kinase NPM1-ALK and acts as a tumor suppressor by reciprocally inhibiting NPM1-ALK expression. Nat Med. 2007;13:1341–1348. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese V, Mallette FA, Deschenes-Simard X, Ramanathan S, Gagnon J, Moores A, et al. SOCS1 links cytokine signaling to p53 and senescence. Mol Cell. 2009;36:754–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
