Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin networks constrain myosin II function in driving retrograde actin flow
- PMID: 22711700
- PMCID: PMC3384413
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201111052
Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin networks constrain myosin II function in driving retrograde actin flow
Abstract
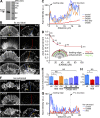
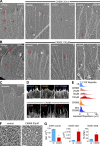
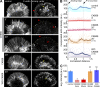
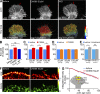
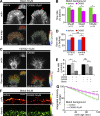
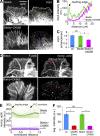
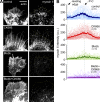
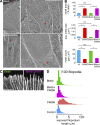
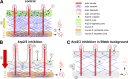
The Arp2/3 complex nucleates actin filaments to generate networks at the leading edge of motile cells. Nonmuscle myosin II produces contractile forces involved in driving actin network translocation. We inhibited the Arp2/3 complex and/or myosin II with small molecules to investigate their respective functions in neuronal growth cone actin dynamics. Inhibition of the Arp2/3 complex with CK666 reduced barbed end actin assembly site density at the leading edge, disrupted actin veils, and resulted in veil retraction. Strikingly, retrograde actin flow rates increased with Arp2/3 complex inhibition; however, when myosin II activity was blocked, Arp2/3 complex inhibition now resulted in slowing of retrograde actin flow and veils no longer retracted. Retrograde flow rate increases induced by Arp2/3 complex inhibition were independent of Rho kinase activity. These results provide evidence that, although the Arp2/3 complex and myosin II are spatially segregated, actin networks assembled by the Arp2/3 complex can restrict myosin II-dependent contractility with consequent effects on growth cone motility.
Figures
References
-
- Bailly M., Macaluso F., Cammer M., Chan A., Segall J.E., Condeelis J.S. 1999. Relationship between Arp2/3 complex and the barbed ends of actin filaments at the leading edge of carcinoma cells after epidermal growth factor stimulation. J. Cell Biol. 145:331–345 10.1083/jcb.145.2.331 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

