Murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle1c2 mediates CD4+ T cell activation and maps to estrogen-related receptor γ
- PMID: 22711888
- PMCID: PMC3392454
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200411
Murine lupus susceptibility locus Sle1c2 mediates CD4+ T cell activation and maps to estrogen-related receptor γ
Abstract
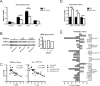
Sle1c is a sublocus of the NZM2410-derived Sle1 major lupus susceptibility locus. We have shown previously that Sle1c contributes to lupus pathogenesis by conferring increased CD4(+) T cell activation and increased susceptibility to chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), which mapped to the centromeric portion of the locus. In this study, we have refined the centromeric sublocus to a 675-kb interval, termed Sle1c2. Mice from recombinant congenic strains expressing Sle1c2 exhibited increased CD4(+) T cell intrinsic activation and cGVHD susceptibility, similar to mice with the parental Sle1c. In addition, B6.Sle1c2 mice displayed a robust expansion of IFN-γ-expressing T cells. NZB complementation studies showed that Sle1c2 expression exacerbated B cell activation, autoantibody production, and renal pathology, verifying that Sle1c2 contributes to lupus pathogenesis. The Sle1c2 interval contains two genes, only one of which, Esrrg, is expressed in T cells. B6.Sle1c2 CD4(+) T cells expressed less Esrrg than B6 CD4(+) T cells, and Esrrg expression was correlated negatively with CD4(+) T cell activation. Esrrg encodes an orphan nuclear receptor that regulates oxidative metabolism and mitochondrial functions. In accordance with reduced Esrrg expression, B6.Sle1c2 CD4(+) T cells present reduced mitochondrial mass and altered mitochondrial functions as well as altered metabolic pathway utilization when compared with B6 CD4(+) T cells. Taken together, we propose Esrrg as a novel lupus susceptibility gene regulating CD4(+) T cell function through their mitochondrial metabolism.
Figures

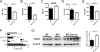
References
-
- Morel L, Rudofsky UH, Longmate JA, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK. Polygenic control of susceptibility to murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity. 1994;1:219–229. - PubMed
-
- Boackle SA, Holers VM, Chen XJ, Szakonyi G, Karp DR, Wakeland EK, Morel L. Cr2, a candidate gene in the murine Sle1c lupus susceptibility locus, encodes a dysfunctional protein. Immunity. 2001;15:775–785. - PubMed
-
- Sobel ES, Mohan C, Morel L, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK. Genetic dissection of SLE pathogenesis: Adoptive transfer of Sle1 mediates the loss of tolerance by bone marrow-derived B cells. J. Immunol. 1999;162:2415–2421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

