The complex actions of sumatriptan on rat dural afferents
- PMID: 22711897
- PMCID: PMC3583198
- DOI: 10.1177/0333102412451356
The complex actions of sumatriptan on rat dural afferents
Abstract
Aim: To test the hypothesis that the clinical efficacy of triptans reflects convergent modulation of ion channels also involved in inflammatory mediator (IM)-induced sensitization of dural afferents.
Methods: Acutely dissociated retrogradely labeled rat dural afferents were studied with whole cell and perforated patch techniques in the absence and presence of sumatriptan and/or IM (prostaglandin E2, bradykinin, and histamine).
Results: Sumatriptan dose-dependently suppressed voltage-gated Ca²⁺ currents. Acute (2 min) sumatriptan application increased dural afferent excitability and occluded further IM-induced sensitization. In contrast, pre-incubation (30 min) with sumatriptan had no influence on dural afferent excitability and partially prevented IM-induced sensitization of dural afferents. The sumatriptan-induced suppression of voltage-gated Ca²⁺ currents and acute sensitization and pre-incubation-induced block of IM-induced sensitization were blocked by the 5-HT(1D) antagonist BRL 15572. Pre-incubation with sumatriptan failed to suppress the IM-induced decrease in action potential threshold and overshoot (which results from modulation of voltage-gated Na⁺ currents) and activation of Cl⁻ current, and had no influence on the Cl⁻ reversal potential. However, pre-incubation with sumatriptan caused a dramatic hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage dependence of K⁺ current activation.
Discussion: These results indicate that although the actions of sumatriptan on dural afferents are complex, at least two distinct mechanisms underlie the antinociceptive actions of this compound. One of these mechanisms, the shift in the voltage dependence of K⁺ channel activation, may suggest a novel strategy for future development of anti-migraine agents.
Figures

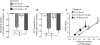
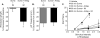


References
-
- Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Scher AI. Epidemiology and economic impact of migraine. Curr Med Res Opin. 2001;17(Suppl 1):s4–12. - PubMed
-
- Galletti F, Cupini LM, Corbelli I, Calabresi P, Sarchielli P. Pathophysiological basis of migraine prophylaxis. Prog Neurobiol. 2009;89:176–92. - PubMed
-
- Tfelt-Hansen P, De Vries P, Saxena PR. Triptans in migraine: a comparative review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Drugs. 2000;60:1259–87. - PubMed
-
- Sarchielli P, Alberti A, Codini M, Floridi A, Gallai V. Nitric oxide metabolites, prostaglandins and trigeminal vasoactive peptides in internal jugular vein blood during spontaneous migraine attacks. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:907–18. - PubMed
-
- Strassman AM, Raymond SA, Burstein R. Sensitization of meningeal sensory neurons and the origin of headaches. Nature. 1996;384:560–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

