Sos7, an essential component of the conserved Schizosaccharomyces pombe Ndc80-MIND-Spc7 complex, identifies a new family of fungal kinetochore proteins
- PMID: 22711988
- PMCID: PMC3434540
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00212-12
Sos7, an essential component of the conserved Schizosaccharomyces pombe Ndc80-MIND-Spc7 complex, identifies a new family of fungal kinetochore proteins
Abstract
Chromosome segregation is powered by the kinetochore, a large macromolecular structure assembled on centromeric chromatin. Attachment of sister chromatids to microtubules is mediated by the highly conserved tripartite KMN (acronym for KNL-1-Mis12-Ndc80) kinetochore network. In the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the equivalent complex is called NMS (Ndc80-MIND-Spc7). Here, we show that not all components of the NMS complex had been identified previously. A 10th NMS component exists, the essential Sos7 protein, which is a genetic and physical interaction partner of Spc7. The analysis of sos7 kinetochore-null mutant yeast strains demonstrated that Sos7 is central to NMS function. In particular, Sos7 is required for kinetochore targeting of Spc7 as well as components of the MIND complex. sos7 mutant strains show severe chromosome missegregation phenotypes and have compromised microtubule-kinetochore interactions. Sos7 is the founding member of a functionally conserved fungal kinetochore family not present in the point centromere carrying Saccharomycotina clusters, suggesting that the new Sos7 family might be a signature motif of fungi with regional centromeres.
Figures





 , coimmunoprecipitation; −, no coimmunoprecipitation. Raw data are shown in Fig. S5 in the supplemental material. (B) Spc7 and Sos7 interact via their C-terminal ends. Yeast 2-hybrid analysis using the indicated fusion constructs. Transformants were grown on synthetic defined medium plates with (control) or without (selective) histidine and adenine for 3 days at 30°C. “AD” and “BD” denote the Gal4 activating and binding domains, respectively. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of differently tagged Sos7 proteins. Protein extracts of a Sos7-cMyc strain expressing plasmid-encoded Sos7-GFP variants were used for immunoprecipitation using anti-cMyc antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot analysis using an anti-GFP antibody. (Right panel) Summary of the interaction of Sos7 variants.
, coimmunoprecipitation; −, no coimmunoprecipitation. Raw data are shown in Fig. S5 in the supplemental material. (B) Spc7 and Sos7 interact via their C-terminal ends. Yeast 2-hybrid analysis using the indicated fusion constructs. Transformants were grown on synthetic defined medium plates with (control) or without (selective) histidine and adenine for 3 days at 30°C. “AD” and “BD” denote the Gal4 activating and binding domains, respectively. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of differently tagged Sos7 proteins. Protein extracts of a Sos7-cMyc strain expressing plasmid-encoded Sos7-GFP variants were used for immunoprecipitation using anti-cMyc antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot analysis using an anti-GFP antibody. (Right panel) Summary of the interaction of Sos7 variants.  , coimmunoprecipitation. Raw data are shown in Fig. S6 in the supplemental material. (D) Yeast 2-hybrid analysis showing Sos7201-264 self-interaction. Transformants were grown on SD plates with (control) or without (selective) histidine for 4 days. V, vector control; AD and BD, activating and binding domain plasmids, respectively.
, coimmunoprecipitation. Raw data are shown in Fig. S6 in the supplemental material. (D) Yeast 2-hybrid analysis showing Sos7201-264 self-interaction. Transformants were grown on SD plates with (control) or without (selective) histidine for 4 days. V, vector control; AD and BD, activating and binding domain plasmids, respectively.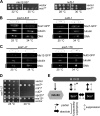

References
-
- Baker DJ, et al. 2004. BubR1 insufficiency causes early onset of aging-associated phenotypes and infertility in mice. Nat. Genet. 36:744–749 - PubMed
-
- Cheeseman IM, Chappie JS, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Desai A. 2006. The conserved KMN network constitutes the core microtubule-binding site of the kinetochore. Cell 127:983–997 - PubMed
-
- DeLuca JG, et al. 2006. Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell 127:969–982 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
