Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by Erlotinib (Tarceva) with Superimposed Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infection in a Pancreatic Cancer Patient: A Case Report
- PMID: 22712013
- PMCID: PMC3376341
- DOI: 10.1159/000338806
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by Erlotinib (Tarceva) with Superimposed Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infection in a Pancreatic Cancer Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
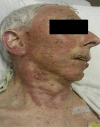
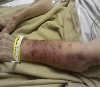
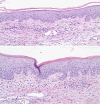
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare acute reaction that is drug induced in 90% of the cases and characterized by a widespread, sterile pustular rash. Erlotinib, a small-molecule EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA for patients with pancreatic cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Skin rash is a well-known side effect related with all EGFR blocking agents. It has been suggested that rash could be used as a surrogate marker for response and possibly be associated with prolonged survival. We report a case of rare presentation of AGEP involving an adverse effect of erlotinib. The commonly reported adverse effects of erlotinib are mild skin eruptions. However, our case describes the rare presentation of AGEP induced by erlotinib. The estimated incidence rate of AGEP is approximately 1-5 cases per million/year.
Keywords: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Erlotinib; Sterile pustular rash; Surrogate marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Erlotinib in a Patient with Lung Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2021 Mar 29;14(1):599-603. doi: 10.1159/000514146. eCollection 2021 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33976640 Free PMC article.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: analysis of cases managed in a tertiary hospital in Singapore.Int J Dermatol. 2010 May;49(5):507-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2010.04313.x. Int J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20534083
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome overlap due to hydroxychloroquine: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2020 Nov 3;14(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02504-8. J Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33138853 Free PMC article.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine: first case report in Canada and review of the literature.J Cutan Med Surg. 2013 Nov-Dec;17(6):414-8. doi: 10.2310/7750.2013.12105. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 24138979 Review.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 Nov;73(5):843-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017. Epub 2015 Sep 6. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26354880 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions induced by targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 May 17;10:1259-1273. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S163391. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 29844705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by icotinib: a case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1462430. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1462430. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39281279 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Drugs Induced Severe Adverse Cutaneous Drug Reactions: An Updated Review on the Risks Associated with Anticancer Targeted Therapy or Immunotherapies.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jan 17;2018:5376476. doi: 10.1155/2018/5376476. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29577050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Erlotinib in a Patient with Lung Cancer.Case Rep Oncol. 2021 Mar 29;14(1):599-603. doi: 10.1159/000514146. eCollection 2021 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33976640 Free PMC article.
-
Management of dermatologic toxicities associated with monoclonal antibody epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: A case review.J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;4(Suppl 1):S78-85. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.120966. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24347989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perez-Soler R. Rash as a surrogate marker for efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2006;8(suppl 1):S7–S14. - PubMed
-
- Burris HA, Jr, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2403–2413. - PubMed
-
- Louvet C, Labianca R, Hammel P, Lledo G, Zampino MG, André T, et al. Gemcitabine in combination with oxaliplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: results of a GERCOR and GISCAD phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3509–3516. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–1966. - PubMed
-
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, Mockenhaupt M, Fagot JP, Roujeau JC. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) – results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR) Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:989–996. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

