Predictors of pregnancy and changes in pregnancy incidence among HIV-positive women accessing HIV clinical care
- PMID: 22713479
- PMCID: PMC3495056
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283565df1
Predictors of pregnancy and changes in pregnancy incidence among HIV-positive women accessing HIV clinical care
Abstract
Objectives: To describe predictors of pregnancy and changes in pregnancy incidence among HIV-positive women accessing HIV clinical care.
Methods: Data were obtained through the linkage of two separate studies: the UK Collaborative HIV Cohort study (UK CHIC), a cohort of adults attending 13 large HIV clinics; and the National Study of HIV in Pregnancy and Childhood (NSHPC), a national surveillance study of HIV-positive pregnant women. Pregnancy incidence was measured using the proportion of women in UK CHIC with a pregnancy reported to NSHPC. Generalized estimating equations were used to identify predictors of pregnancy and assess changes in pregnancy incidence in 2000-2009.
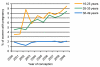
Results: The number of women accessing care at UK CHIC sites increased as did the number of pregnancies. Older women were less likely to have a pregnancy [adjusted relative rate (aRR) 0.44 per 10 year increment in age, [95% confidence interval (CI) (0.41-0.46)], P < 0.001] as were women with CD4 cell count less than 200 cells/μl compared with CD4 cell count 200-350 cells/μl [aRR 0.65 (0.55-0.77), P < 0.001] and women of white ethnicity compared with women of black African ethnicity [aRR 0.67 (0.57-0.80), P < 0.001]. The likelihood that women had a pregnancy increased over the study period [aRR 1.05 (1.03-1.07), P < 0.001). The rate of change did not significantly differ according to age group, antiretroviral therapy use, CD4 group or ethnicity.
Conclusion: The pregnancy rate among women accessing HIV clinical care increased in 2000-2009. HIV-positive women with, or planning, a pregnancy require a high level of care and this is likely to continue and increase as more women of older age have pregnancies.
Figures
References
-
- Health Protection Agency . SOPHID: Accessing HIV care national tables: 2010. [Last accessed April 2012]. 2011. Available at www.hpa.org.uk.
-
- Health Protection Agency . HIV in the United Kingdom: 2011 Report. [Last accessed April 2012]. 2011. Available at www.hpa.org.uk.
-
- Gazzard BG, BHIVA Treatment Guidelines Writing Group British HIV Association Guidelines for the treatment of HIV-1-infected adults with antiretroviral therapy 2008. HIV Med. 2008;9(8):563–608. - PubMed
-
- Clumeck N, Pozniak A, Raffi F. European AIDS Clinical Society (EACS) guidelines for the clinical management and treatment of HIV-infected adults. HIV Med. 2008;9(2):65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials