Radioluminescent nanophosphors enable multiplexed small-animal imaging
- PMID: 22714145
- PMCID: PMC3482915
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.20.011598
Radioluminescent nanophosphors enable multiplexed small-animal imaging
Abstract
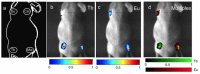
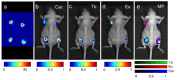
We demonstrate the ability to image multiple nanoparticle-based contrast agents simultaneously using a nanophosphor platform excited by either radiopharmaceutical or X-ray irradiation. These radioluminescent nanoparticles emit optical light at unique wavelengths depending on their lanthanide dopant, enabling multiplexed imaging. This study demonstrates the separation of two distinct nanophosphor contrast agents in gelatin phantoms with a recovered phosphor separation correlation of -0.98. The ability to distinguish the two nanophosphors and a Cerenkov component is then demonstrated in a small animal phantom. Combined with the high-resolution potential of low-scattering X-ray excitation, this imaging technique may be a promising method to probe molecular processes in living organisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cerenkov luminescence tomography for small-animal imaging.Opt Lett. 2010 Apr 1;35(7):1109-11. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.001109. Opt Lett. 2010. PMID: 20364233 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity evaluation and selective plane imaging geometry for x-ray-induced luminescence imaging.Med Phys. 2017 Oct;44(10):5367-5377. doi: 10.1002/mp.12470. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28703922 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo 3-Dimensional Radiopharmaceutical-Excited Fluorescence Tomography.J Nucl Med. 2017 Jan;58(1):169-174. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.116.180596. Epub 2016 Sep 22. J Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 27660137
-
Fluorescence and Cerenkov luminescence imaging. Applications in small animal research.Nuklearmedizin. 2016;55(2):63-70. Nuklearmedizin. 2016. PMID: 27067794 Review.
-
Comparison of Gallium-68 and Fluorine-18 imaging characteristics in positron emission tomography.Appl Radiat Isot. 2013 Jun;76:55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2012.06.034. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Appl Radiat Isot. 2013. PMID: 23063597 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Radioluminescent CaF2:Ln Core, Mesoporous Silica Shell Nanoparticles for Use in X-ray Based Theranostics.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jul 24;10(8):1447. doi: 10.3390/nano10081447. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722132 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed imaging of radionuclides.Nat Biomed Eng. 2025 Jul;9(7):993-1006. doi: 10.1038/s41551-025-01406-8. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Nat Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40542108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring pH-triggered drug release from radioluminescent nanocapsules with X-ray excited optical luminescence.ACS Nano. 2013 Feb 26;7(2):1178-87. doi: 10.1021/nn304369m. Epub 2013 Jan 9. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 23281651 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsically 89Zr-labeled Gd2O2S:Eu nanophosphors with high in vivo stability for dual-modality imaging.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Dec 15;8(12):5591-5600. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 28078029 Free PMC article.
-
Tb-Doped core-shell-shell nanophosphors for enhanced X-ray induced luminescence and sensitization of radiodynamic therapy.Biomater Sci. 2021 Jan 26;9(2):496-505. doi: 10.1039/d0bm00897d. Biomater Sci. 2021. PMID: 33006335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stroh M., Zimmer J. P., Duda D. G., Levchenko T. S., Cohen K. S., Brown E. B., Scadden D. T., Torchilin V. P., Bawendi M. G., Fukumura D., Jain R. K., “Quantum dots spectrally distinguish multiple species within the tumor milieu in vivo,” Nat. Med. 11(6), 678–682 (2005).10.1038/nm1247 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

