Three routes to suppression of the neurodegenerative phenotypes caused by kinesin heavy chain mutations
- PMID: 22714410
- PMCID: PMC3430534
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.112.140798
Three routes to suppression of the neurodegenerative phenotypes caused by kinesin heavy chain mutations
Abstract
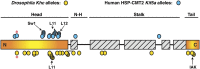
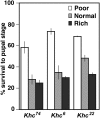
Kinesin-1 is a motor protein that moves stepwise along microtubules by employing dimerized kinesin heavy chain (Khc) subunits that alternate cycles of microtubule binding, conformational change, and ATP hydrolysis. Mutations in the Drosophila Khc gene are known to cause distal paralysis and lethality preceded by the occurrence of dystrophic axon terminals, reduced axonal transport, organelle-filled axonal swellings, and impaired action potential propagation. Mutations in the equivalent human gene, Kif5A, result in similar problems that cause hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) and Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2 (CMT2) distal neuropathies. By comparing the phenotypes and the complementation behaviors of a large set of Khc missense alleles, including one that is identical to a human Kif5A HSP allele, we identified three routes to suppression of Khc phenotypes: nutrient restriction, genetic background manipulation, and a remarkable intramolecular complementation between mutations known or likely to cause reciprocal changes in the rate of microtubule-stimulated ADP release by kinesin-1. Our results reveal the value of large-scale complementation analysis for gaining insight into protein structure-function relationships in vivo and point to possible paths for suppressing symptoms of HSP and related distal neuropathies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spastic paraplegia mutation N256S in the neuronal microtubule motor KIF5A disrupts axonal transport in a Drosophila HSP model.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003066. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23209432 Free PMC article.
-
Role of kinesin heavy chain in Crumbs localization along the rhabdomere elongation in Drosophila photoreceptor.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021218. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695062 Free PMC article.
-
Role of kinesin-1-based microtubule sliding in Drosophila nervous system development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):E4985-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522416113. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27512046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of kinesin-1 in the pathogenesis of SPG10, a rare form of hereditary spastic paraplegia.Neuroscientist. 2013 Aug;19(4):336-44. doi: 10.1177/1073858412451655. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Neuroscientist. 2013. PMID: 22785106 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics and inherited peripheral nerve diseases.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Jun 2;596:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25847151 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual control of Kinesin-1 recruitment to microtubules by Ensconsin in Drosophila neuroblasts and oocytes.Development. 2019 Apr 17;146(8):dev171579. doi: 10.1242/dev.171579. Development. 2019. PMID: 30936181 Free PMC article.
-
Common general anesthetic propofol impairs kinesin processivity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 23;114(21):E4281-E4287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701482114. Epub 2017 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28484025 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of kinesin switch I mutations that cause hereditary spastic paraplegia.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 5;12(7):e0180353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180353. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28678816 Free PMC article.
-
Spastic paraplegia mutation N256S in the neuronal microtubule motor KIF5A disrupts axonal transport in a Drosophila HSP model.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003066. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23209432 Free PMC article.
-
Pavarotti/MKLP1 regulates microtubule sliding and neurite outgrowth in Drosophila neurons.Curr Biol. 2015 Jan 19;25(2):200-205. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25557664 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

