Regulation of the mTOR-Rac1 axis in platelet function
- PMID: 22714420
- PMCID: PMC3398921
- DOI: 10.4161/sgtp.19137
Regulation of the mTOR-Rac1 axis in platelet function
Abstract
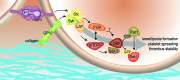
Small GTPase proteins regulate cytoskeletal dynamics to orchestrate diverse cellular functions in organismal physiology, development and disease. The Rho GTPase family member Rac1 is central to actin-driven processes in a number of cell types, particularly platelets, where Rac1 serves as an essential mediator of lamellipodia formation and thrombus stability. Despite the importance of Rac1 to platelet function, little is known about how Rac1 activity is regulated in platelets. We recently defined the tyrosine-kinase based signaling cascade that activates mTOR to regulate Rac1 activation downstream of platelet integrin and glycoprotein receptors. We demonstrated a critical role for the mTOR-Rac1 axis in regulating platelet spreading, aggregation and aggregate stability under shear. These studies suggest that in addition to cancer and transplant medicine, intervention of the mTOR system may have implications for hemostatic and thrombotic processes as well as immunotherapies and intravascular stent design.
Figures
Comment on
-
S6K1 and mTOR regulate Rac1-driven platelet activation and aggregation.Blood. 2011 Sep 15;118(11):3129-36. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-331579. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21757621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schoenwaelder SM, Hughan SC, Boniface K, Fernando S, Holdsworth M, Thompson PE, et al. RhoA sustains integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 adhesion contacts under high shear. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:14738–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
