Flurbiprofen, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, protects mice from hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting GSK-3β signaling and mitochondrial permeability transition
- PMID: 22714712
- PMCID: PMC3474435
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00088
Flurbiprofen, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, protects mice from hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting GSK-3β signaling and mitochondrial permeability transition
Abstract
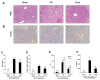
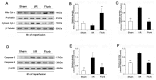
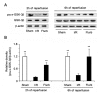
Flurbiprofen acts as a nonselective inhibitor for cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2), but its impact on hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains unclear. Mice were randomized into sham, I/R and flurbiprofen (Flurb) groups. The hepatic artery and portal vein to the left and median liver lobes were occluded for 90 min and unclamped for reperfusion to establish a model of segmental (70%) warm hepatic ischemia. Pretreatment of animals with flurbiprofen prior to I/R insult significantly decreased serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and prevented hepatocytes from I/R-induced apoptosis/necrosis. Moreover, flurbiprofen dramatically inhibited mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) pore opening, and thus prevented mitochondrial-related cell death and apoptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that flurbiprofen markedly inhibited glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β activity and increased phosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser9, which, consequently, could modulate the adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT)-cyclophilin D (CyP-D) complex and the susceptibility to MPT induction. Therefore, administration of flurbiprofen prior to hepatic I/R ameliorates mitochondrial and hepatocellular damage through inhibition of MPT and inactivation of GSK-3β, and provides experimental evidence for clinical use of flurbiprofen to protect liver function in surgical settings in addition to its conventional use for pain relief.
Figures





References
-
- Caldwell-Kenkel JC, Currin RT, Tanaka Y, Thurman RG, Lemasters JJ. Kupffer cell activation and endothelial cell damage after storage of rat livers: effects of reperfusion. Hepatology. 1991;13:83–95. - PubMed
-
- Liu DL, Jeppsson B, Hakansson CH, Odselius R. Multiple-system organ damage resulting from prolonged hepatic inflow interruption. Arch Surg. 1996;131:442–7. - PubMed
-
- Glantzounis GK, Salacinski HJ, Yang W, Davidson BR, Seifalian AM. The contemporary role of antioxidant therapy in attenuating liver ischemia-reperfusion injury: a review. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:1031–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

