Influence of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the changes of blood pressure in rats
- PMID: 2271508
- PMCID: PMC4534999
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1990.5.1.23
Influence of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the changes of blood pressure in rats
Abstract
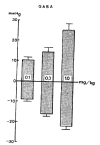
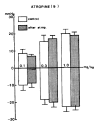
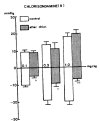
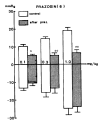
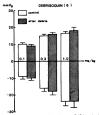
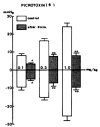
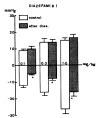
This is an attempt to investigate the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a well-known major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, on the blood pressure response in rats and to elucidate the mechanism of its action. GABA injected into a femoral vein of the rat produced a dose-related fall in blood pressure followed by a secondary pressor response. The depressor response evoked by GABA was clearly blocked by pretreatment with chlorisondamine, diazepam and picrotoxin but was unaffected by atropine, prazosin and debrisoquin. GABA-induced pressor responses were significantly attenuated by pretreatment with prazosin or picrotoxin, while not affected by atropine, diazepam, debrisoquin and chlorisondamine. These experimental data suggest that GABA causes biphasically depressor and pressor responses in rats, and that the hypotensive activity evoked by GABA may be exerted through activation of GABAergic receptors and hypertensive activity due to stimulation of the adrenergic alpha-receptors, which appears to be associated with GABAergic receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Enna SJ, Maggi A. Minireview: Biochemical pharmacology of GABA-ergic agonists. Life Sci. 1979;24:1727. - PubMed
-
- Tappaz M, Brownstein MJ, Kopin IJ. Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in discrete nuclei of hypothalamus and substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1977;125:109. - PubMed
-
- Cheramy E, Nieoullon A, Glowinski J. GABAergic processes involved in the control of dopamine release from nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in the cat. European J Pharmacol. 1978;48:281. - PubMed
-
- Soubrie P, Montastruc J-L, Bourgoin S, Reisine T, Artaud first initial, Glowinski J. In vivo evidence GABAergic control of serotonin reease in the cat substan nigra. European J Pharmacol. 1981;69:483. - PubMed
-
- Sangiah S, Borowitz JL, Yim GKW. Actions of GABA, picrotoxin and bicuculline on adrenal medulla. European J Pharmacol. 1974;27:130–135. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
