Calpain inhibition attenuated morphological and molecular changes in skeletal muscle of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis rats
- PMID: 22715087
- PMCID: PMC12010168
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.23096
Calpain inhibition attenuated morphological and molecular changes in skeletal muscle of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis rats
Abstract
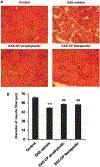
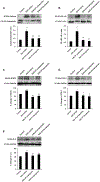
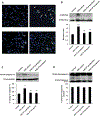
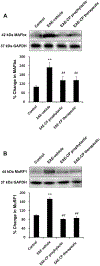
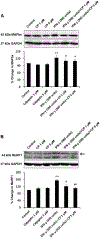
Muscle weakness and atrophy are important manifestations of multiple sclerosis (MS). To investigate the pathophysiological mechanisms of skeletal muscle change in MS, we induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in Lewis male rats and examined morphological and molecular changes in skeletal muscle. We also treated EAE rats with calpepetin, a calpain inhibitor, to examine its beneficial effects on skeletal muscle damage. Morphological changes in muscle tissue of EAE rats included smaller and irregularly shaped muscle fibers and fibrosis. Western blot analysis demonstrated increased calpain:calpastatin ratio, inflammation-related transcription factors (nuclear factor-κB:inhibitor of κB α ratio), and proinflammatory enzymes (cyclooxygenase-2). TUNEL-positive myonuclei in skeletal muscle cells of EAE rats indicated cell death. In addition, markers of apoptotic cell death (Bax:Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-12 protein levels) were elevated. Expression of muscle-specific ubiquitin ligases (muscle atrophy F-box and muscle ring finger protein 1), was upregulated in muscle tissue of EAE-vehicle animals. Both prophylactic and therapeutic treatment with calpeptin partially attenuated muscle changes noted in EAE animals. These results indicate that morphological and molecular changes including apoptotic cell death and protein breakdown develop in skeletal muscle of EAE animals and that these changes can be reversed by calpain inhibition.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Allen DL, Linderman JK, Roy RR, Grindeland RE, Mukku V, Edgerton VR. 1997. Growth hormone/IGF-I and/or resistive exercise maintains myonuclear number in hindlimb unweighted muscles. J Appl Physiol 83:1857–1861. - PubMed
-
- Alway SE, Degens H, Krishnamurthy G, Chaudhrai A. 2003a. Denervation stimulates apoptosis but not Id2 expression in hindlimb muscles of aged rats. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci 58:687–697. - PubMed
-
- Alway SE, Martyn JK, Ouyang J, Chaudhrai A, Murlasits ZS. 2003b. Id2 expression during apoptosis and satellite cell activation in unloaded and loaded quail skeletal muscles. AmJ Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284:R540–R549. - PubMed
-
- Ashley Z, Sutherland H, Lanmuller H, Russold MF, Unger E, Bijak M, Mayr W, Boncompagni S, Protasi F, Salmons S, Jarvis JC. 2007. Atrophy, but not necrosis, in rabbit skeletal muscle denervated for periods up to one year. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C440–C451. - PubMed
-
- Bartoli M, Richard I. 2005. Calpains in muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2115–2133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

