Leptospirosis in Chonbuk Province of Korea in 1987
- PMID: 2271509
- PMCID: PMC4534998
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1990.5.1.34
Leptospirosis in Chonbuk Province of Korea in 1987
Abstract
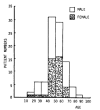
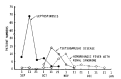
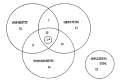
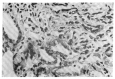
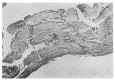
Leptospirosis is a zoonosis with protean clinical manifestations. Its diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion and is confirmed by isolation of the organism or, more commonly, by serologic tests. In the fall of 1987, after severe flooding, we saw 93 patients with leptospirosis, confirmed by a microagglutination test. Thirteen percent of the patients had no clinical or laboratory findings except fever and headache, but the rest had mild to severe manifestations. Jaundice, renal failure, and aseptic meningitis were not common, but pulmonary symptoms, when present, were striking. The mortality rate was 5%. The main cause of death was asphyxiation due to massive hemoptysis from pulmonary hemorrhage and acute respiratory failure.
Figures


References
-
- Takaki I. The Prevalence of Causative Agents in Rat Bite Fever and Icterohaemorrhagic Spirochetae in Seoul. J Chosun Med Assoc. 1919;28:1.
-
- Ro YM, Yuk SJ, et al. Acute Febrile Hemorrhagic Lung Disease of Unknown Cause. J Korean Med Assoc (in Korea) 1976;19:315–323.
-
- Kim MJ. Clinical Characteristics of Leptospirosis in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc (in Korea) 1988;31:623–627.
-
- Kim JS, Lee JW, Oh Dk, In SD, Lee YH, Cho WH. An Epidemiological Study on Identification of Cause for Epidemic Pulmonary Hemorrhagic Fever. J Korean Med Assoc (in Korea) 1985;28:77–87.
-
- Guidelines for the Control of Leptospirosis. WHO Offset Publ. 1983;67:1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
