Serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 2271510
- PMCID: PMC4534993
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1990.5.1.44
Serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
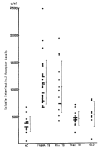
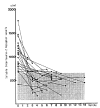
It is well known that the activation of cell mediated immunity has an important role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary tuberculosis and the production of the protective immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. During the activation of T-cell by Interleukin-1 released from the macrophage, not only Interleukin-2 but also the soluble Interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) molecule is released into the extracellular fluid. In vitro study reveals that the level of this sIL-2R is well correlated with the degree of activation of the T-cell. We therefore carried out this study to evaluate the significance of the serum IL-2R level in determining the disease activity of pulmonary tuberculosis. The level of sIL-2R was measured by sandwich ELISA method. The level of sIL-2R in 42 patients with bacteriologically -proven active pulmonary tuberculosis (29 far and moderately advanced pulmonary tuberculosis, age: 30.3 +/- 10.3 yrs; 13 minimal pulmonary tuberculosis, age: 34.4 +/- 15.3 yrs) was 1111 +/- 424 mu/ml, which was significantly higher than the normal control group (age: 31.0 +/- 9.9 yrs) (365 +/- 143 mu/ml) and inactive pulmonary tuberculosis group (age: 37.3 +/- 16.9 yrs) (465 +/- 131 mu/ml). But there was no significant difference between 29 patients with advanced pulmonary tuberculosis (1138 +/- 405 mu/ml) and 13 patients with minimal pulmonary tuberculosis (1051 +/- 474 mu/ml).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor in patients with pulmonary mycobacterial diseases].Kekkaku. 1999 Jun;74(6):499-505. Kekkaku. 1999. PMID: 10423961 Japanese.
-
[Study on the level of soluble interleukin-2 receptor, expression of membrane interleukin-2 receptor and T lymphocyte subpopulations in pulmonary tuberculosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1996 Feb;19(1):44-6. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1996. PMID: 9275389 Chinese.
-
Correlation of serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-4 and soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels with radiologic and clinical manifestations in active pulmonary tuberculosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2003 Feb;12(1):9-14. doi: 10.1080/0962935031000096926. Mediators Inflamm. 2003. PMID: 12745543 Free PMC article.
-
[Changes and significance of peripheral blood T cell subsets, soluble interleukin-2 receptor and interferon-gamma in patients with retreatment pulmonary tuberculosis and initial treatment tuberculosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;34(12):884-7. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22333498 Chinese.
-
T lymphocyte activation in patients with active tuberculosis.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):458-60. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.458. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. PMID: 1859075
Cited by
-
The clinical significance of plasma sCD25 as valuable biomarker for progression and prognosis of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08798-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38254003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Status of Tuberculosis in Korea (1985). Yearbook of health and social statistics Vol 33. Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Republic of Korea
-
- Daniel TM, Debanne SM. The serodiagnosis of tuberculosis and other mycobacterial disease by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;135:1137. - PubMed
-
- Ma Y, Wang YM, Daniel TM. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 5 for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in China. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;134:1273. - PubMed
-
- Kalish SB, Radin RC, Levitz D, Zeiss CR, Phair JP. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method for IgG antibody to purified protein derivative in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tuberculous meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1983;99:630. - PubMed
-
- Yong AJ, Grange M, Tee RD, Beck JS, Bothamley GH, Kemeny DM, Kardjito T. Total and antimycobacterial IgE levels in serum from patients with tuberculosis and leprosy. Tubercle. 1989;70:273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
