Urinary plasminogen activator activity in progressive renal failure
- PMID: 2271512
- PMCID: PMC4534997
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1990.5.1.58
Urinary plasminogen activator activity in progressive renal failure
Abstract
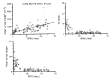
The purpose of this study was to discover how functional nephrons produce the plasminogen activator as renal function progresses to renal failure. Urine Plasminogen activator (U-PA) activity was measured by the fibrin plate method in 73 patients with various degrees of renal function deterioration from various underlying diseases and in one healthy individual in order to evaluate the plasminogen activator activity of remnant nephrons. The plasminogen activator activity of the 12 consecutive urine samples from the healthy individual showed that is varied according to the time of day, but there was no circadian rhythm. The urine plasminogen activator activity correlated with the osmolality (r = 0.51, P less than 0.001) and creatinine (r = 0.56, P less than 0.001) of the urine, suggesting that it is concentrated at distal nephrons. The fractional sodium excretion rate (FeNa) increased abruptly when GFR decreased below 25 L/day. This pattern was very similar with the relation between total U-PA activity/GFR and GFR. The correlation between total U-PA activity and FeNa was not significant, but there was a significant direct correlation between total U-PA activity/GFR and FeNa (r = 0.775, P less than 0.0001). There was no relationship between the 24-hour urine protein and total U-PA activity or total U-PA activity/GFR.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures



References
-
- Lesuk A, Terminiellol, Traver JH. Crystalline human urokinase: Some properties. Science. 1965;147:880. - PubMed
-
- White WF, Barlow GH, Mozen MM. The isolation and characterization of plasminogen activators (urokinase) from human urine. Biochemistry. 1966;5:2160. - PubMed
-
- Bergstein JM, Michael AF., Jr Cortical fibrinolytic activity in normal and diseased human kidneys. J Lab Clin Med. 1972;79701 - PubMed
-
- Bergstein JM, Michael AF., Jr Renal cortical fibrinolytic activity in the rabbit following one or two doses of endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973;29:27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
