CD4+ CD25- FoxP3+ regulatory cells are the predominant responding regulatory T cells after human rotavirus infection or vaccination in gnotobiotic pigs
- PMID: 22716916
- PMCID: PMC3461397
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03617.x
CD4+ CD25- FoxP3+ regulatory cells are the predominant responding regulatory T cells after human rotavirus infection or vaccination in gnotobiotic pigs
Abstract
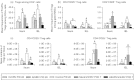
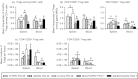
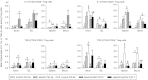
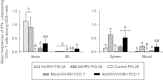
The distribution and dynamic changes of CD4(+) CD25(+) FoxP3(+) and CD4(+) CD25(-) FoxP3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells induced by human rotavirus (HRV) infection and vaccination were examined in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs infected with virulent HRV (VirHRV) or vaccinated with attenuated HRV (AttHRV). Subsets of gnotobiotic pigs in the AttHRV and control groups were challenged with VirHRV at post-inoculation day (PID) 28. We demonstrated that VirHRV infection or AttHRV vaccination reduced frequencies and numbers of tissue-residing Treg cells, and decreased the frequencies of interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) producing CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells in ileum, spleen and blood at PID 28. The frequencies of IL-10 and TGF-β producing CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells in all sites at PID 28 were significantly inversely correlated with the protection rate against VirHRV-caused diarrhoea (r = -1, P < 0.0001). Hence, higher frequencies of functional CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells can be an indicator for poorer protective immunity against rotavirus. Our results highlighted the importance of CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells over CD4(+) CD25(+) Treg cells in rotavirus infection and immunity. AttHRV vaccination (induction of immune effector responses) reduced the expansion of CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells in ileum seen in the challenged naive pigs during the acute phase of VirHRV infection and preserved normal levels of intestinal TGF-β producing Treg cells post-challenge. The reduced suppressive effect of Treg cells in AttHRV-vaccinated pigs would unleash effector/memory T-cell activation upon challenge. Preserving TGF-β producing CD4(+) CD25(-) Treg cells is important in maintaining homeostasis. Based on our findings, a model is proposed to depict the dynamic equilibrium course of Treg and effector T-cell responses after primary rotavirus infection/vaccination and challenge.
© 2012 The Authors. Immunology © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine responses in gnotobiotic pigs after infection with virulent or attenuated human rotavirus.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(1):372-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.372-382.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16352562 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Dosage Affects the Adjuvanticity and Protection Against Rotavirus Diarrhea in Gnotobiotic Pigs.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Jun;60(6):834-43. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000694. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25564808
-
Virus-specific intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cell responses induced by human rotavirus infection and vaccines are correlated with protection against rotavirus diarrhea in gnotobiotic pigs.Vaccine. 2008 Jun 19;26(26):3322-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.03.085. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18456375 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells and the induction of IL-17.Mucosal Immunol. 2008 Nov;1 Suppl 1:S43-6. doi: 10.1038/mi.2008.51. Mucosal Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19079228 Review.
-
Changes of regulatory T cells, transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Immunol. 2016 Sep;170:61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27498109
Cited by
-
The Immune System in Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury Prevention and Therapy: Update and Perspective.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 24;8:639976. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.639976. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33842545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pig model mimicking chronic hepatitis E virus infection in immunocompromised patients to assess immune correlates during chronicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 3;114(27):6914-6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705446114. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28630341 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the cytokine expression of peripheral Treg and Th17 cells in children with rotavirus enteritis.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Aug;10(2):679-682. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2511. Epub 2015 May 22. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622374 Free PMC article.
-
Protein deficiency reduces efficacy of oral attenuated human rotavirus vaccine in a human infant fecal microbiota transplanted gnotobiotic pig model.Vaccine. 2018 Oct 8;36(42):6270-6281. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 30219368 Free PMC article.
-
CD4(+)CD25(-)Foxp3(+) T cells play a role in tuberculous hydrothorax rather than malignant hydrothorax.J Transl Med. 2015 Aug 18;13:268. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0618-6. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26283421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parashar UD, Burton A, Lanata C, Boschi-Pinto C, Shibuya K, Steele D, Birmingham M, Glass RI. Global mortality associated with rotavirus disease among children in 2004. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(Suppl. 1):S9–15. - PubMed
-
- Gray J, Vesikari T, Van Damme P, et al. Rotavirus. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;46(Suppl. 2):S24–31. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, Stevenson G, Saif L. Rotavirus and reovirus. In: Straw BE, Zimmerman JJ, D'Allaire S, Taylor DJ, editors. Diseases of Swine. 9th edn. Ames, IA: Blackwell Publishing; 2006. pp. 435–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

