Blood pressure levels and mortality risk among hemodialysis patients in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study
- PMID: 22718187
- PMCID: PMC3891306
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2012.136
Blood pressure levels and mortality risk among hemodialysis patients in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study
Abstract
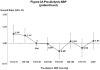
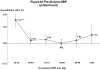
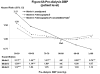
KDOQI practice guidelines recommend predialysis blood pressure <140/90 mm Hg; however, most prior studies had found elevated mortality with low, not high, systolic blood pressure. This is possibly due to unmeasured confounders affecting systolic blood pressure and mortality. To lessen this bias, we analyzed 24,525 patients by Cox regression models adjusted for patient and facility characteristics. Compared with predialysis systolic blood pressure of 130-159 mm Hg, mortality was 13% higher in facilities with 20% more patients at systolic blood pressure of 110-129 mm Hg and 16% higher in facilities with 20% more patients at systolic blood pressure of ≥160 mm Hg. For patient-level systolic blood pressure, mortality was elevated at low (<130 mm Hg), not high (≥180 mm Hg), systolic blood pressure. For predialysis diastolic blood pressure, mortality was lowest at 60-99 mm Hg, a wide range implying less chance to improve outcomes. Higher mortality at systolic blood pressure of <130 mm Hg is consistent with prior studies and may be due to excessive blood pressure lowering during dialysis. The lowest risk facility systolic blood pressure of 130-159 mm Hg indicates this range may be optimal, but may have been influenced by unmeasured facility practices. While additional study is needed, our findings contrast with KDOQI blood pressure targets, and provide guidance on optimal blood pressure range in the absence of definitive clinical trial data.
Figures


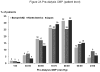
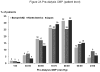









References
-
- Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, et al. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet. 2002;360:1347–1360. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, et al. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Renal Data System. USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive Disease and Kidney Diseases; 2009.
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45:S1–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

