Structure of the nuclear factor κB-inducing kinase (NIK) kinase domain reveals a constitutively active conformation
- PMID: 22718757
- PMCID: PMC3431628
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.366658
Structure of the nuclear factor κB-inducing kinase (NIK) kinase domain reveals a constitutively active conformation
Abstract
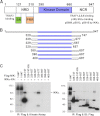
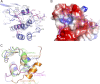
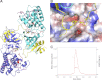
NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) is a central component in the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Excessive NIK activity is implicated in various disorders, such as autoimmune conditions and cancers. Here, we report the first crystal structure of truncated human NIK in complex with adenosine 5'-O-(thiotriphosphate) at a resolution of 2.5 Å. This truncated protein is a catalytically active construct, including an N-terminal extension of 60 residues prior to the kinase domain, the kinase domain, and 20 residues afterward. The structure reveals that the NIK kinase domain assumes an active conformation in the absence of any phosphorylation. Analysis of the structure uncovers a unique role for the N-terminal extension sequence, which stabilizes helix αC in the active orientation and keeps the kinase domain in the catalytically competent conformation. Our findings shed light on the long-standing debate over whether NIK is a constitutively active kinase. They also provide a molecular basis for the recent observation of gain-of-function activity for an N-terminal deletion mutant (ΔN324) of NIK, leading to constitutive non-canonical NF-κB signaling with enhanced B-cell adhesion and apoptosis resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Vallabhapurapu S., Karin M. (2009) Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 693–733 - PubMed
-
- Hayden M. S., Ghosh S. (2008) Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell 132, 344–362 - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi G., Karin M. (2004) The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 25, 280–288 - PubMed
-
- Senftleben U., Cao Y., Xiao G., Greten F. R., Krähn G., Bonizzi G., Chen Y., Hu Y., Fong A., Sun S. C., Karin M. (2001) Activation by IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κB signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 - PubMed
-
- Pomerantz J. L., Baltimore D. (2002) Two pathways to NF-κB. Mol. Cell 10, 693–695 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

