Generation of biotechnology-derived Flavobacterium columnare ghosts by PhiX174 gene E-mediated inactivation and the potential as vaccine candidates against infection in grass carp
- PMID: 22719209
- PMCID: PMC3376489
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/760730
Generation of biotechnology-derived Flavobacterium columnare ghosts by PhiX174 gene E-mediated inactivation and the potential as vaccine candidates against infection in grass carp
Abstract
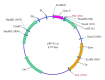
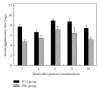
Flavobacterium columnare is a bacterial pathogen causing high mortality rates for many freshwater fish species. Fish vaccination with a safe and effective vaccine is a potential approach for prevention and control of fish disease. Here, in order to produce bacterial ghost vaccine, a specific Flavobacterium lysis plasmid pBV-E-cat was constructed by cloning PhiX174 lysis gene E and the cat gene with the promoter of F. columnare into the prokaryotic expression vector pBV220. The plasmid was successfully electroporated into the strain F. columnare G4cpN22 after curing of its endogenous plasmid. F. columnare G4cpN22 ghosts (FCGs) were generated for the first time by gene E-mediated lysis, and the vaccine potential of FCG was investigated in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) by intraperitoneal route. Fish immunized with FCG showed significantly higher serum agglutination titers and bactericidal activity than fish immunized with FKC or PBS. Most importantly, after challenge with the parent strain G4, the relative percent survival (RPS) of fish in FCG group (70.9%) was significantly higher than FKC group (41.9%). These results showed that FCG could confer immune protection against F. columnare infection. As a nonliving whole cell envelope preparation, FCG may provide an ideal alternative to pathogen-based vaccines against columnaris in aquaculture.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Generation and immunity effect evaluation of biotechnology-derived Aeromonas veronii ghost by PhiX174 gene E-mediated inactivation in koi (Cyprinus carprio koi).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Mar;86:327-334. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.07.042. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30041051
-
Identification of immunogenic proteins of Flavobacterium columnare by two-dimensional electrophoresis immunoblotting with antibacterial sera from grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes).J Fish Dis. 2012 Apr;35(4):255-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2011.01340.x. Epub 2012 Jan 31. J Fish Dis. 2012. PMID: 22288818
-
Immunization of eyed channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, eggs with monovalent Flavobacterium columnare vaccine and bivalent F. columnare and Edwardsiella ictaluri vaccine.Vaccine. 2007 Jan 22;25(6):1126-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.09.055. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17050050
-
An Overview of Vaccine Development Strategies for Columnaris-Causing Bacteria in Cultured Fish.J Fish Dis. 2025 Aug;48(8):e14155. doi: 10.1111/jfd.14155. Epub 2025 May 30. J Fish Dis. 2025. PMID: 40448373 Review.
-
Flavobacterium psychrophilum vaccine development: a difficult task.Microb Biotechnol. 2014 Sep;7(5):414-23. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12099. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Microb Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25056179 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of Lactobacillus casei ghosts by Holin-mediated inactivation and the potential as a safe and effective vehicle for the delivery of DNA vaccines.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Jul 28;18(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1216-6. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30055567 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Defense Functions of the Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) DnaJ B9b and DnaJ C3a Genes in Response to Pathogenic Bacteria under High-Temperature Stress Conditions.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 13;11(10):1509. doi: 10.3390/biom11101509. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680142 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Chemically-Induced Bacterial Ghosts (BGs) Using Sodium Hydroxide-Induced Vibrio parahaemolyticus Ghosts (VPGs).Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 15;17(11):1904. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111904. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27854308 Free PMC article.
-
A Salmonella typhimurium ghost vaccine induces cytokine expression in vitro and immune responses in vivo and protects rats against homologous and heterologous challenges.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 29;12(9):e0185488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185488. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28961267 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided vaccine designing approach against fish pathogens Edwardsiella tarda and Flavobacterium columnare using bioinformatics softwares.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 May 23;10:1703-14. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S95691. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27284239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durborow RM, Thune RL, Hawke JP, Camus AC. Publication. 479. Stoneville, Mich, USA: Aquaculture Center; 1998. Columnaris disease: a bacterial infection caused by Flavobacterium columnare.
-
- Austin B, Austin DA. Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish. Edinburgh, UK: Heriot-Watt University; 1999.
-
- Gaikowski MP, Larson WJ, Gingerich WH. Survival of cool and warm freshwater fish following chloramine-T exposure. Aquaculture. 2008;275(1–4):20–25.
-
- Darwish AM, Mitchell AJ, Straus DL. Evaluation of potassium permanganate against an experimental subacute infection of Flavobacterium columnare in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque) Journal of Fish Diseases. 2009;32(2):193–199. - PubMed
-
- Darwish AM, Mitchell AJ. Evaluation of diquat against an acute experimental infection of Flavobacterium columnare in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque) Journal of Fish Diseases. 2009;32(5):401–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

