Diosgenin Induces Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells through Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Pathway
- PMID: 22719792
- PMCID: PMC3375183
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/981675
Diosgenin Induces Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells through Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondrial Pathway
Abstract
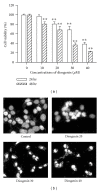
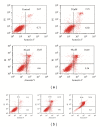
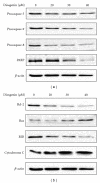
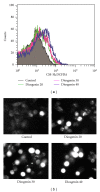
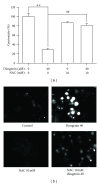
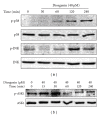
Diosgenin, a naturally occurring steroid saponin found abundantly in legumes and yams, is a precursor of various synthetic steroidal drugs. Diosgenin is studied for the mechanism of its action in apoptotic pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Based on DAPI staining, diosgenin-treated cells manifested nuclear shrinkage, condensation, and fragmentation. Treatment of HepG2 cells with 40 μM diosgenin resulted in activation of the caspase-3, -8, -9 and cleavage of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and the release of cytochrome c. In the upstream, diosgenin increased the expression of Bax, decreased the expression of Bid and Bcl-2, and augmented the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Diosgenin-induced, dose-dependent induction of apoptosis was accompanied by sustained phosphorylation of JNK, p38 MAPK and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK)-1, as well as generation of the ROS. NAC administration, a scavenger of ROS, reversed diosgene-induced cell death. These results suggest that diosgenin-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through Bcl-2 protein family-mediated mitochndria/caspase-3-dependent pathway. Also, diosgenin strongly generated ROS and this oxidative stress might induce apoptosis through activation of ASK1, which are critical upstream signals for JNK/p38 MAPK activation in HepG2 cancer cells.
Figures
References
-
- Raju J, Mehta R. Cancer chemopreventive and therapeutic effects of diosgenin, a food saponin. Nutrition and Cancer. 2009;61(1):27–35. - PubMed
-
- Accatino L, Pizarro M, Solís N, Koenig CS. Effects of diosgenin, a plant-derived steroid, on bile secretion and hepatocellular cholestasis induced by estrogens in the rat. Hepatology. 1998;28(1):129–140. - PubMed
-
- Turchan J, Pocernich CB, Gairola C, et al. Oxidative stress in HIV demented patients and protection ex vivo with novel antioxidants. Neurology. 2003;60(2):307–314. - PubMed
-
- Corbiere C, Liagre B, Bianchi A, et al. Different contribution of apoptosis to the antiproliferative effects of diosgenin and other plant steroids, hecogenin and tigogenin, on human 1547 osteosarcoma cells. International Journal of Oncology. 2003;22(4):899–905. - PubMed
-
- Wang SL, Cai B, Cui CB, Liu HW, Wu CF, Yao XS. Diosgenin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β -D-glucopyranoside obtained as a new anticancer agent from Dioscorea futschauensis induces apoptosis on human colon carcinoma HCT-15 cells via mitochondria-controlled apoptotic pathway. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research. 2004;6(2):115–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

