Upregulation of miR-31* is negatively associated with recurrent/newly formed oral leukoplakia
- PMID: 22719913
- PMCID: PMC3377716
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038648
Upregulation of miR-31* is negatively associated with recurrent/newly formed oral leukoplakia
Abstract
Background: Oral leukoplakia (OLK) is a potentially malignant disorder of the oral cavity. However, the underlying mechanism of OLK is still unclear. In this study, we explore possible miRNAs involved in OLK.
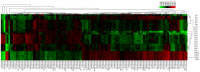
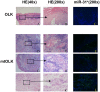
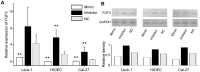
Methodology/principal findings: Using miRNA microarrays, we profiled miRNA expression in OLK and malignantly transformed OLK (mtOLK) tissue samples. The upregulation of miR-31*, miR-142-5p, miR-33a, miR-1259, miR-146b-5p, miR-886-3p, miR-886-5p, miR-519d, and miR-301a along with the downregulation of miR-572, miR-611, miR-602, miR-675, miR-585, miR-623, miR-637, and miR-1184 in mtOLK were new observations. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analyses confirmed that miR-31* is highly expressed in mtOLK. There was a significant difference between the FISH score (p<0.05) in patients with or without recurrent/newly formed OLK. Functional analyses demonstrated that a miR-31* inhibitor decreased apoptosis in the Leuk-1, which is an immortalized oral epithelial cell line spontaneously derived from an oral leukoplakia lesion. miR-31* regulated apoptosis, cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in the HOIEC, which is a HPV E6/E7-immortalized oral epithelial cell line. Furthermore, miR-31* modulated the biological functions of apoptosis, cell proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in the oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line, Cal-27. Using bioinformatic analyses and dual luciferase reporter assays, we determined that the 3' untranslated region of fibroblast growth factor 3 (FGF3) is the target of miR-31*. Expression of FGF3 was downregulated or upregulated in the presence of a miR-31* mimic or inhibitor, respectively.
Conclusions/significance: Upregulation of miR-31* is negatively associated with recurrent/newly formed OLK. MiR-31* may exert similar but distinguishable effects on biological function in oral cells with different malignant potential. FGF3 is the target of miR-31*. miR-31* may play an important role during OLK progression through regulating FGF3. MiRNA* strands may also have prominent roles in oral carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional annotation analysis of their targets associated with the malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia.Gene. 2015 Mar 10;558(2):271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25576219
-
A three miRNAs signature for predicting the transformation of oral leukoplakia to oral squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 1;8(8):1403-1413. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30210912 Free PMC article.
-
CircHLA-C: A significantly upregulated circRNA co-existing in oral leukoplakia and oral lichen planus.Organogenesis. 2023 Dec 31;19(1):2234504. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2023.2234504. Organogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37531467 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated expression and functions of microRNA-330 in cancers: A potential therapeutic target.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Feb;146:112600. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112600. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34968919
-
The global prevalence of oral leukoplakia: a systematic review and meta-analysis from 1996 to 2022.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Sep 6;23(1):645. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03342-y. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37670255 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
World Workshop on Oral Medicine VII: Prognostic biomarkers in oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of longitudinal studies.Oral Dis. 2019 Jun;25 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):64-78. doi: 10.1111/odi.13087. Oral Dis. 2019. PMID: 31140698 Free PMC article.
-
Altered peritumoral microRNA expression predicts head and neck cancer patients with a high risk of recurrence.Mod Pathol. 2017 Oct;30(10):1387-1401. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.62. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Mod Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28731048
-
MicroRNA: a connecting road between apoptosis and cholesterol metabolism.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):8529-54. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4988-z. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27105614 Review.
-
Periodontitis and oral cancer - current concepts of the etiopathogenesis.Oncol Rev. 2020 Mar 18;14(1):465. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2020.465. eCollection 2020 Feb 18. Oncol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32231765 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Important Players and Biomarkers in Oral Carcinogenesis.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:186904. doi: 10.1155/2015/186904. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26504785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Califano J, van der Riet P, Westra W, Nawroz H, Clayman G, et al. Genetic progression model for head and neck cancer: implications for field cancerization. Cancer research. 1996;56:2488. - PubMed
-
- Kramer IR, Lucas RB, Pindborg JJ, Sobin LH. Definition of leukoplakia and related lesions: an aid to studies on oral precancer. Oral surgery, oral medicine, and oral pathology. 1978;46:518. - PubMed
-
- Van der Hem PS, Nauta JM, der Wal JE, Roodenburg JLN. The results of CO2 laser surgery in patients with oral leukoplakia: a 25 year follow up. Oral oncology. 2005;41:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Neville BW, Day TA. Oral cancer and precancerous lesions. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2002;52:195–215. - PubMed
-
- Chen CZ. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. The New England Journal of Medicine 353. 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

