Deficient dopamine D2 receptor function causes renal inflammation independently of high blood pressure
- PMID: 22719934
- PMCID: PMC3375266
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038745
Deficient dopamine D2 receptor function causes renal inflammation independently of high blood pressure
Abstract
Renal dopamine receptors participate in the regulation of blood pressure. Genetic factors, including polymorphisms of the dopamine D(2) receptor gene (DRD2) are associated with essential hypertension, but the mechanisms of their contribution are incompletely understood. Mice lacking Drd2 (D(2)-/-) have elevated blood pressure, increased renal expression of inflammatory factors, and renal injury. We tested the hypothesis that decreased dopamine D(2) receptor (D(2)R) function increases vulnerability to renal inflammation independently of blood pressure, is an immediate cause of renal injury, and contributes to the subsequent development of hypertension. In D(2)-/- mice, treatment with apocynin normalized blood pressure and decreased oxidative stress, but did not affect the expression of inflammatory factors. In mouse RPTCs Drd2 silencing increased the expression of TNFα and MCP-1, while treatment with a D(2)R agonist abolished the angiotensin II-induced increase in TNF-α and MCP-1. In uni-nephrectomized wild-type mice, selective Drd2 silencing by subcapsular infusion of Drd2 siRNA into the remaining kidney produced the same increase in renal cytokines/chemokines that occurs after Drd2 deletion, increased the expression of markers of renal injury, and increased blood pressure. Moreover, in mice with two intact kidneys, short-term Drd2 silencing in one kidney, leaving the other kidney undisturbed, induced inflammatory factors and markers of renal injury in the treated kidney without increasing blood pressure. Our results demonstrate that the impact of decreased D(2)R function on renal inflammation is a primary effect, not necessarily associated with enhanced oxidant activity, or blood pressure; renal damage is the cause, not the result, of hypertension. Deficient renal D(2)R function may be of clinical relevance since common polymorphisms of the human DRD2 gene result in decreased D(2)R expression and function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
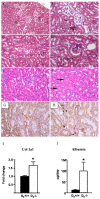




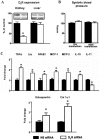
References
-
- Li XX, Bek M, Asico LD, Yang Z, Grandy DK, et al. Adrenergic and endothelin B receptor-dependent hypertension in dopamine receptor type-2 knockout mice. Hypertension. 2001;38:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Armando I, Wang X, Villar VA, Jones JE, Asico LD, et al. Reactive oxygen species-dependent hypertension in dopamine D2 receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension. 2007;49:672–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK039308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL068686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL074940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL092196/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092196/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK090918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK039308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

