Identification of karyopherin α1 and α7 interacting proteins in porcine tissue
- PMID: 22720010
- PMCID: PMC3374799
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038990
Identification of karyopherin α1 and α7 interacting proteins in porcine tissue
Abstract
Specialized trafficking systems in eukaryotic cells serve a critical role in partitioning intracellular proteins between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic proteins (including chromatin remodeling enzymes and transcription factors) must gain access to the nucleus to exert their functions to properly program fundamental cellular events ranging from cell cycle progression to gene transcription. Knowing that nuclear import mediated by members of the karyopherin α family of transport receptors plays a critical role in regulating development and differentiation, we wanted to determine the identity of proteins that are trafficked by this karyopherin α pathway. To this end, we performed a GST pull-down assay using porcine orthologs of karyopherin α1 (KPNA1) and karyopherin α7 (KPNA7) and prey protein derived from porcine fibroblast cells and used a liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) approach to determine the identity of KPNA1 and KPNA7 interacting proteins. Our screen revealed that the proteins that interact with KPNA1 and KPNA7 are generally nuclear proteins that possess nuclear localization signals. We further validated two candidate proteins from this screen and showed that they are able to be imported into the nucleus in vivo and also interact with members of the karyopherin α family of proteins in vitro. Our results also reveal the utility of using a GST pull-down approach coupled with LC-MS/MS to screen for protein interaction partners in a non-traditional model system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
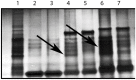
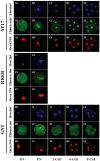
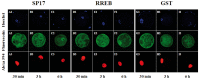
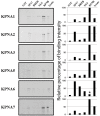
Similar articles
-
KPNA7, an oocyte- and embryo-specific karyopherin α subtype, is required for porcine embryo development.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2012;24(2):382-91. doi: 10.1071/RD11119. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2012. PMID: 22281085
-
Nuclear import of prototype foamy virus transactivator Bel1 is mediated by KPNA1, KPNA6 and KPNA7.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):399-406. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2635. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Int J Mol Med. 2016. Retraction in: Int J Mol Med. 2017 Mar;39(3):771. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2860. PMID: 27277550 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Nsp1β inhibits interferon-activated JAK/STAT signal transduction by inducing karyopherin-α1 degradation.J Virol. 2013 May;87(9):5219-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02643-12. Epub 2013 Feb 28. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23449802 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct nuclear import and export pathways mediated by members of the karyopherin beta family.J Cell Biochem. 1998 Aug 1;70(2):231-9. J Cell Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9671229 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of nuclear protein transport.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997;7(1-2):61-72. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v7.i1-2.40. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997. PMID: 9034715 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific peroxidases differentiate Brachypodium distachyon accessions and are associated with drought tolerance traits.Ann Bot. 2016 Aug;118(2):259-70. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw104. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Ann Bot. 2016. PMID: 27325900 Free PMC article.
-
Sterile α Motif Domain Containing 9 Is a Novel Cellular Interacting Partner to Low-Risk Type Human Papillomavirus E6 Proteins.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149859. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26901061 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cargo proteins specific for importin-β with importin-α applying a stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based in vitro transport system.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24540-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.489286. Epub 2013 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23846694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lachner M, Jenuwein T. The many faces of histone lysine methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14(3):286–298. - PubMed
-
- Klochendler-Yeivin A, Muchardt C, Yaniv M. SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling and cancer. Curr Opin Gene and Dev. 2002;12:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Nigg E. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: Signals, mechanisms and regulation. Nature. 1997;386:779–786. - PubMed
-
- Moroianu J. Distinct nuclear import and export pathways mediated by members of the karyopherin β family. J Cell Biochem. 1998;70:231–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

