Rickettsiae induce microvascular hyperpermeability via phosphorylation of VE-cadherins: evidence from atomic force microscopy and biochemical studies
- PMID: 22720111
- PMCID: PMC3373609
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001699
Rickettsiae induce microvascular hyperpermeability via phosphorylation of VE-cadherins: evidence from atomic force microscopy and biochemical studies
Abstract
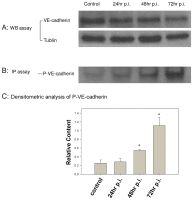
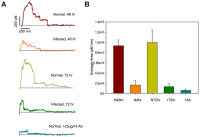
The most prominent pathophysiological effect of spotted fever group (SFG) rickettsial infection of microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) is an enhanced vascular permeability, promoting vasogenic cerebral edema and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, which are responsible for most of the morbidity and mortality in severe cases. To date, the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which SFG Rickettsia increase EC permeability are largely unknown. In the present study we used atomic force microscopy (AFM) to study the interactive forces between vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin and human cerebral microvascular EC infected with R. montanensis, which is genetically similar to R. rickettsii and R. conorii, and displays a similar ability to invade cells, but is non-pathogenic and can be experimentally manipulated under Biosafety Level 2 (BSL2) conditions. We found that infected ECs show a significant decrease in VE-cadherin-EC interactions. In addition, we applied immunofluorescent staining, immunoprecipitation phosphorylation assay, and an in vitro endothelial permeability assay to study the biochemical mechanisms that may participate in the enhanced vascular permeability as an underlying pathologic alteration of SFG rickettsial infection. A major finding is that infection of R. montanensis significantly activated tyrosine phosphorylation of VE-cadherin beginning at 48 hr and reaching a peak at 72 hr p.i. In vitro permeability assay showed an enhanced microvascular permeability at 72 hr p.i. On the other hand, AFM experiments showed a dramatic reduction in VE-cadherin-EC interactive forces at 48 hr p.i. We conclude that upon infection by SFG rickettsiae, phosphorylation of VE-cadherin directly attenuates homophilic protein-protein interactions at the endothelial adherens junctions, and may lead to endothelial paracellular barrier dysfunction causing microvascular hyperpermeability. These new approaches should prove useful in characterizing the antigenically related SFG rickettsiae R. conorii and R. rickettsii in a BSL3 environment. Future studies may lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies to inhibit the VE-cadherin-associated microvascular hyperpermeability in SFG rickettsioses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Compartmentalized, functional role of angiogenin during spotted fever group rickettsia-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction: evidence of possible mediation by host tRNA-derived small noncoding RNAs.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Jun 23;13:285. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-285. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23800282 Free PMC article.
-
VE-cadherin Y685F knock-in mouse is sensitive to vascular permeability in recurrent angiogenic organs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;307(3):H455-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00774.2013. Epub 2014 May 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24858856
-
HIV-1 Tat C phosphorylates VE-cadherin complex and increases human brain microvascular endothelial cell permeability.BMC Neurosci. 2014 Jun 26;15:80. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-80. BMC Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24965120 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
-
Rap1 Small GTPase Regulates Vascular Endothelial-Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions and Vascular Permeability.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(10):1371-1379. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00504. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34602545 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii Dysregulates Barrier Function and Mechanotransduction Signaling in Human Endothelial Cells.mSphere. 2020 Jan 29;5(1):e00550-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00550-19. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 31996420 Free PMC article.
-
Benidipine impairs innate immunity converting sublethal to lethal infections in a murine model of spotted fever rickettsiosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Feb 26;18(2):e0011993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011993. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38408129 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferons promote severe disease in a mouse model of lethal ehrlichiosis.Infect Immun. 2014 Apr;82(4):1698-709. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01564-13. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24491580 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP plays a critical role in bacterial invasion during fatal rickettsioses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 26;110(48):19615-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314400110. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24218580 Free PMC article.
-
A new role for host annexin A2 in establishing bacterial adhesion to vascular endothelial cells: lines of evidence from atomic force microscopy and an in vivo study.Lab Invest. 2019 Nov;99(11):1650-1660. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0284-z. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Lab Invest. 2019. PMID: 31253864 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

