T cells and T cell tumors efficiently generate antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell immunity when modified with an NKT ligand
- PMID: 22720235
- PMCID: PMC3376985
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.1.2.18479
T cells and T cell tumors efficiently generate antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell immunity when modified with an NKT ligand
Abstract
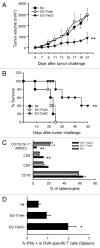
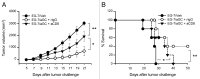
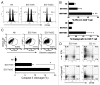
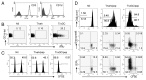
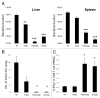
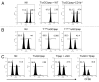
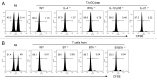
Various Invariant NKT (iNKT) cell ligands have been shown as potent adjuvants in boosting T cell reactivates to antigens on professional APC. Non-professional APC, such as T cells, also co-expressing MHC class I and CD1d, have been unattractive cell vaccine carriers due to their poor immunogenicity. Here, we report that T cells as well as T cell lymphoma can efficiently generate antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) responses in mice in vivo, when formulated to present iNKT ligand α-galactosylceramide (αGC) on their surface CD1d. Vaccination with αGC-pulsed EG-7 T-cell lymphoma induced tumor-specific CTL response and suppressed the growth of EG-7 in a CD8 T cell-dependent manner. Injection of αGC-loaded CD4 T cells in mice efficiently activated iNKT cells in vivo. While T cells loaded with a class I-restricted peptide induced proliferation but not effector differentiation of antigen-specific CD8 T cells, injection of T cells co-pulsed with αGC strongly induced IFNγ and Granzyme B expression in T cells and complete lysis of target cells in vivo. Presentation of αGC and peptide on the same cells was required for optimal CTL response and vaccinating T cells appeared to directly stimulate both iNKT and cytotoxic CD8 T cells. Of note, the generation of this cytotoxic T cell response was independent of IL-4, IFNγ, IL-12, IL-21 and costimulation. Our data indicate that iNKT cell can license a non-professional APC to directly trigger antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell responses, which provides an alternative cellular vaccine strategy against tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Fujii S, Shimizu K, Smith C, Bonifaz L, Steinman RM. Activation of natural killer T cells by alpha-galactosylceramide rapidly induces the full maturation of dendritic cells in vivo and thereby acts as an adjuvant for combined CD4 and CD8 T cell immunity to a coadministered protein. J Exp Med. 2003;198:267–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030324. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang DH, Osman K, Connolly J, Kukreja A, Krasovsky J, Pack M, et al. Sustained expansion of NKT cells and antigen-specific T cells after injection of alpha-galactosyl-ceramide loaded mature dendritic cells in cancer patients. J Exp Med. 2005;201:1503–17. doi: 10.1084/jem.20042592. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
