Pretreatment with intrathecal amitriptyline potentiates anti-hyperalgesic effects of post-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline following spinal nerve ligation
- PMID: 22720761
- PMCID: PMC3519508
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-12-44
Pretreatment with intrathecal amitriptyline potentiates anti-hyperalgesic effects of post-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline following spinal nerve ligation
Abstract
Background: Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant and potent use-dependent blocker of sodium channels, has been shown to attenuate acute and chronic pain in several preclinical modes. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether intrathecal pretreatment with amitriptyline combined with post-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline is more effective than post-injury treatment alone on L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL)-induced neuropathic pain.
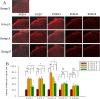
Methods: 96 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated into 4 groups: group S, Sham; group L, L5 spinal nerve Ligation with vehicle treatment; group A, SNL and post-injury intra-peritoneal (Abdominal) amitriptyline twice daily × 3 days; group P, intrathecal Pretreatment with amitriptyline, SNL and intra-peritoneal amitriptyline twice daily × 3 days. Responses to thermal and mechanical stimuli, as well as sodium channel expression in injured dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and activated glial cells in spinal dorsal horn (SDH) were measured pre-operatively and on post-operative day (POD) 4, 7, 14, 21 and 28.
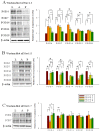
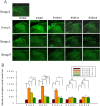
Results: SNL-evoked hyper-sensitivity responses to thermal and mechanical stimuli, up-regulated Nav1.3 and down-regulated Nav1.8 expression in DRG, and activated microglia and astrocytes in SDH. In group A, intra-peritoneal amitriptyline alone alleviated thermal hypersensitivity on POD7, reversed Nav1.8 and reduced activated microglia on POD14. In group P, intrathecal pretreatment with amitriptyline not only potentiated the effect of intra-peritoneal amitriptyline on thermal hypersensitivity and Nav1.8, but attenuated mechanical hypersensitivity on POD7 and reduced up-regulated Nav1.3 on POD14. Furthermore, this treatment regimen reduced astrocyte activation on POD14.
Conclusions: Concomitant intrathecal pretreatment and post-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline was more effective than post-injury treatment alone on attenuation of behavioral hypersensitivity, decrease of activated microglia and astrocytes and dysregulated Nav1.3 and 1.8.
Figures
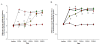
References
-
- Benedetti F, Vighetti S, Amanzio M, Casadio C, Oliaro A, Bergamasco B, Maggi G. Dose–response relationship of opioids in nociceptive and neuropathic postoperative pain. Pain. 1998;74(2–3):205–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

