Role of intramyocelluar lipids in human health
- PMID: 22721584
- PMCID: PMC4908975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.05.009
Role of intramyocelluar lipids in human health
Abstract
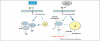
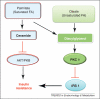
Intramyocellular lipid (IMCL) is predominantly stored as intramuscular triglyceride (IMTG) in lipid droplets and is utilized as metabolic fuel during physical exercise. IMTG is also implicated in muscle insulin resistance (IR) in type 2 diabetes. However, it has become apparent that lipid moieties such as ceramide and diacylglycerol are the likely culprits of IR. This article reviews current knowledge of IMCL-mediated IR and important areas of investigation, including myocellular lipid transport and lipid droplet proteins. Several crucial questions remain unanswered, such as the identity of specific ceramide and diacylglycerol species that mediate IR in human muscle and their subcellular location. Quantitative lipidomics and proteomics of targeted subcellular organelles will help to better define the mechanisms underlying pathological IMCL accumulation and IR.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kissebah AH, Krakower GR. Regional adiposity and morbidity. Physiol. Rev. 1994;74:761–811. - PubMed
-
- Webber J. Energy balance in obesity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003;62:539–543. - PubMed
-
- de Ferranti S, Mozaffarian D. The perfect storm: obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin. Chem. 2008;54:945–955. - PubMed
-
- Glatz JF, et al. Membrane fatty acid transporters as regulators of lipid metabolism: implications for metabolic disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010;90:367–417. - PubMed
-
- Dyck DJ, et al. Functional differences in lipid metabolism in resting skeletal muscle of various fiber types. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:E340–E351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

