Two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography separation and tandem mass spectrometry detection of atrazine and its metabolic and hydrolysis products in urine
- PMID: 22721710
- PMCID: PMC4528303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.05.028
Two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography separation and tandem mass spectrometry detection of atrazine and its metabolic and hydrolysis products in urine
Abstract
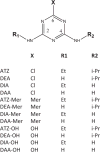
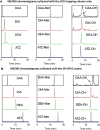
Atrazine [6-chloro-N-ethyl-N'-(1-methylethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine] is the most widely used herbicide in the United States. In recent years, there has been controversy about atrazine's potential endocrine/reproductive and neurological adverse effects in wildlife and humans. The controversy triggered several environmental and epidemiologic studies, and it generated needs for sensitive and selective analytical methods for the quantification of atrazine, atrazine metabolites, and degradation or hydrolysis products. We developed a two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography (2D-HPLC) method with isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry detection to measure atrazine in urine, along with 11 atrazine metabolites and hydrolysis products, including 6-chloro (Cl), 6-mercapto (Mer) and 6-hydroxy (OH) derivatives, and their desethyl, desisopropyl and diamino atrazine analogs (DEA, DIA and DAA, respectively). The 2D-HPLC system incorporated strong cation exchange and reversed phase separation modes. This versatile approach can be used for the quantitative determination of all 12 compounds in experimental animals for toxicological studies. The method requires only 10 μL of urine, and the limits of detection (LODs) range from 10 to 50 μg/L. The method can also be applied to assess atrazine exposure in occupational settings by measurement of 6-Cl and 6-Mer analogs, which requires only 100 μL of urine with LODs of 1-5 μg/L. Finally, in combination with automated off-line solid phase extraction before 2D-HPLC, the method can also be applied in non-occupational environmental exposure studies for the determination of -6-Cl and 6-Mer metabolites, using 500 μL of urine and LODs of 0.1-0.5 μg/L.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantification of atrazine, phenylurea, and sulfonylurea herbicide metabolites in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Anal Toxicol. 2007 May;31(4):181-6. doi: 10.1093/jat/31.4.181. J Anal Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17555640
-
An improved high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method to measure atrazine and its metabolites in human urine.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010 Apr 15;878(13-14):957-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.02.025. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20299293
-
Quantification of atrazine and its metabolites in urine by on-line solid-phase extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008 Jul;391(5):1931-9. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2102-0. Epub 2008 May 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18454284
-
Infiltration and adsorption of dissolved atrazine and atrazine metabolites in buffalograss filter strips.J Environ Qual. 2003 Nov-Dec;32(6):2319-24. doi: 10.2134/jeq2003.2319. J Environ Qual. 2003. PMID: 14674556
-
On-line solid-phase extraction method for determination of triazine herbicides and degradation products in seawater by ultra-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2016 Oct 28;1470:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 6. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 27726863
Cited by
-
Real-Time Monitoring of the Atrazine Degradation by Liquid Chromatography and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Effect of Fenton Process and Ultrasound Treatment.Molecules. 2022 Dec 17;27(24):9021. doi: 10.3390/molecules27249021. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558153 Free PMC article.
-
Mercapturic acids: recent advances in their determination by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and their use in toxicant metabolism studies and in occupational and environmental exposure studies.Biomarkers. 2016;21(4):293-315. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2016.1141988. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Biomarkers. 2016. PMID: 26900903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and Pharmacological Comparison of Human, Mouse, and Rat Organic Cation Transporter 1 toward Drug and Pesticide Interaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 19;21(18):6871. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186871. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961667 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of mercapturic acid biomarkers in occupational and environmental exposure monitoring.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Aug 1;964:136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.02.057. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24746702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun CNT embedded ZnO nanofiber based biosensor for electrochemical detection of Atrazine: a step closure to single molecule detection.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2020 Jan 13;6:3. doi: 10.1038/s41378-019-0115-9. eCollection 2020. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2020. PMID: 34567618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erickson BE. Chem Eng News. 2010;88:31.
-
- Sathiakumar N, MacLennan PA, Mandel J, Delzell E. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2011;41:1. - PubMed
-
- Government Document, US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Atrazine. 2003 - PubMed
-
- Web Page, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S.EPA) Cumulative Risk from Triazine Pesticides. 2006
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

