Human α-defensin 6 promotes mucosal innate immunity through self-assembled peptide nanonets
- PMID: 22722251
- PMCID: PMC4332406
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1218831
Human α-defensin 6 promotes mucosal innate immunity through self-assembled peptide nanonets
Abstract
Defensins are antimicrobial peptides that contribute broadly to innate immunity, including protection of mucosal tissues. Human α-defensin (HD) 6 is highly expressed by secretory Paneth cells of the small intestine. However, in contrast to the other defensins, it lacks appreciable bactericidal activity. Nevertheless, we report here that HD6 affords protection against invasion by enteric bacterial pathogens in vitro and in vivo. After stochastic binding to bacterial surface proteins, HD6 undergoes ordered self-assembly to form fibrils and nanonets that surround and entangle bacteria. This self-assembly mechanism occurs in vivo, requires histidine-27, and is consistent with x-ray crystallography data. These findings support a key role for HD6 in protecting the small intestine against invasion by diverse enteric pathogens and may explain the conservation of HD6 throughout Hominidae evolution.
Figures
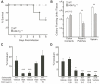
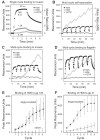
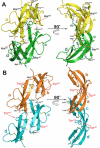
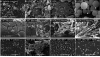
Comment in
-
Immunology. HD6 defensin nanonets.Science. 2012 Jul 27;337(6093):420-1. doi: 10.1126/science.1225906. Science. 2012. PMID: 22837514 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lehrer RI, Bevins CL, Ganz T. In: Mucosal Immunology. 3rd Mestecky J, et al., editors. Vol. 1. Academic Press; New York: 2004. pp. 95–110.
-
- Ouellette AJ. Paneth cells and innate mucosal immunity. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2010;26:547. - PubMed
-
- Bevins CL, Salzman NH. Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:356. - PubMed
-
- Wehkamp J, Stange EF. Paneth's disease. J. Crohns Colitis. 2010;4:523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI082320/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI050843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI057757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI073120/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI070726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HD059127/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI088122/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076246/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI073120/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072732/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040124/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI060555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI088122/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076246/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI082320/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI072732/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI032738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI032738/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI057757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099526/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD059127/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

