S-phase sensing of DNA-protein crosslinks triggers TopBP1-independent ATR activation and p53-mediated cell death by formaldehyde
- PMID: 22722496
- PMCID: PMC3404879
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.20905
S-phase sensing of DNA-protein crosslinks triggers TopBP1-independent ATR activation and p53-mediated cell death by formaldehyde
Abstract
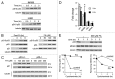
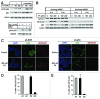
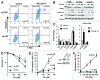
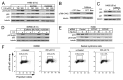
We examined genotoxic signaling and cell fate decisions in response to a potent DNA-protein crosslinker formaldehyde (FA). DNA-protein crosslinks (DPC) are poorly understood lesions produced by bifunctional carcinogens and several cancer drugs. FA-treated human cells showed a rapid activation of ATR kinase that preferentially targeted the p53 transcription factor at low doses and CHK1 kinase at more severe damage, producing bell-shaped and sublinear responses, respectively. CHK1 phosphorylation was transient, and its loss was accompanied by increased p53 accumulation and Ser15 phosphorylation. Activation of p53 was insensitive to inhibition of mismatch repair and nucleotide and base excision repair, excluding the role of small DNA adducts in this response. The p53-targeted signaling was transcription-independent, absent in quiescent cells and specific to S-phase in cycling populations. Unlike other S-phase stressors, FA-activated p53 was functional transcriptionally, promoted apoptosis in lung epithelial cells and caused senescence in normal lung fibroblasts. FA did not induce ATR, RAD1 or RPA foci, and p53 phosphorylation was TopBP1-independent, indicating a noncanonical mode of ATR activation. Replication arrest by FA caused a dissociation of ATR from a chromatin-loaded MCM helicase but no PCNA monoubiquitination associated with stalled polymerases. These results suggest that unlike typical DNA adducts that stall DNA polymerases, replication inhibition by bulkier DPC largely results from blocking upstream MCM helicase, which prevents accumulation of ssDNA. Overall, our findings indicate that S-phase-specific, TopBP1-independent activation of the ATR-p53 axis is a critical stress response to FA-DPC, which has implications for understanding of FA carcinogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decarbamoyl mitomycin C (DMC) activates p53-independent ataxia telangiectasia and rad3 related protein (ATR) chromatin eviction.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(5):744-54. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2014.997517. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25565400 Free PMC article.
-
RHINO forms a stoichiometric complex with the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp and mediates ATR-Chk1 signaling.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(1):99-108. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.967076. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25602520 Free PMC article.
-
5-ASA affects cell cycle progression in colorectal cells by reversibly activating a replication checkpoint.Gastroenterology. 2007 Jan;132(1):221-35. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.10.016. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17241873 Free PMC article.
-
TopBP1 and DNA polymerase alpha-mediated recruitment of the 9-1-1 complex to stalled replication forks: implications for a replication restart-based mechanism for ATR checkpoint activation.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 15;8(18):2877-84. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.18.9485. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19652550 Review.
-
Mechanisms of ATR-mediated checkpoint signalling.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010 Jun 1;15(3):840-53. doi: 10.2741/3649. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010. PMID: 20515729 Review.
Cited by
-
Formaldehyde Is a Potent Proteotoxic Stressor Causing Rapid Heat Shock Transcription Factor 1 Activation and Lys48-Linked Polyubiquitination of Proteins.Am J Pathol. 2016 Nov;186(11):2857-2868. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27639166 Free PMC article.
-
Phyto-Phospholipid Conjugated Scorpion Venom Nanovesicles as Promising Carrier That Improves Efficacy of Thymoquinone against Adenocarcinoma Human Alveolar Basal Epithelial Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 13;13(12):2144. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122144. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959424 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin C increases DNA breaks and suppresses DNA damage-independent activation of ATM by bleomycin.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 May 20;136:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.03.026. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30926564 Free PMC article.
-
Nickel-induced HIF-1α promotes growth arrest and senescence in normal human cells but lacks toxic effects in transformed cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;331:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.029. Epub 2017 May 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28552779 Free PMC article.
-
Monoubiquitinated H2B, a Main Chromatin Target of Formaldehyde, Is Important for S-Phase Checkpoint Signaling and Genome Stability.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Dec;63(12):2414-2424. doi: 10.1002/mc.23819. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 39254477
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
